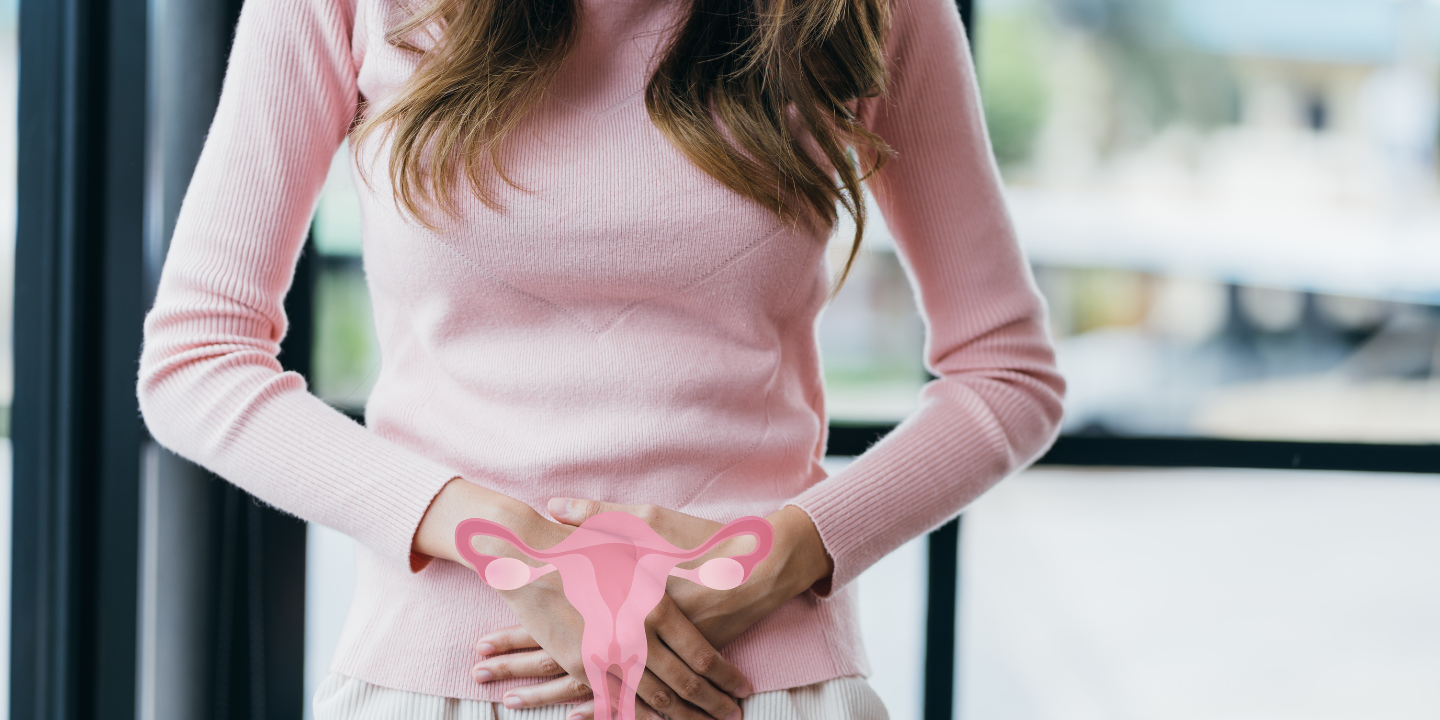
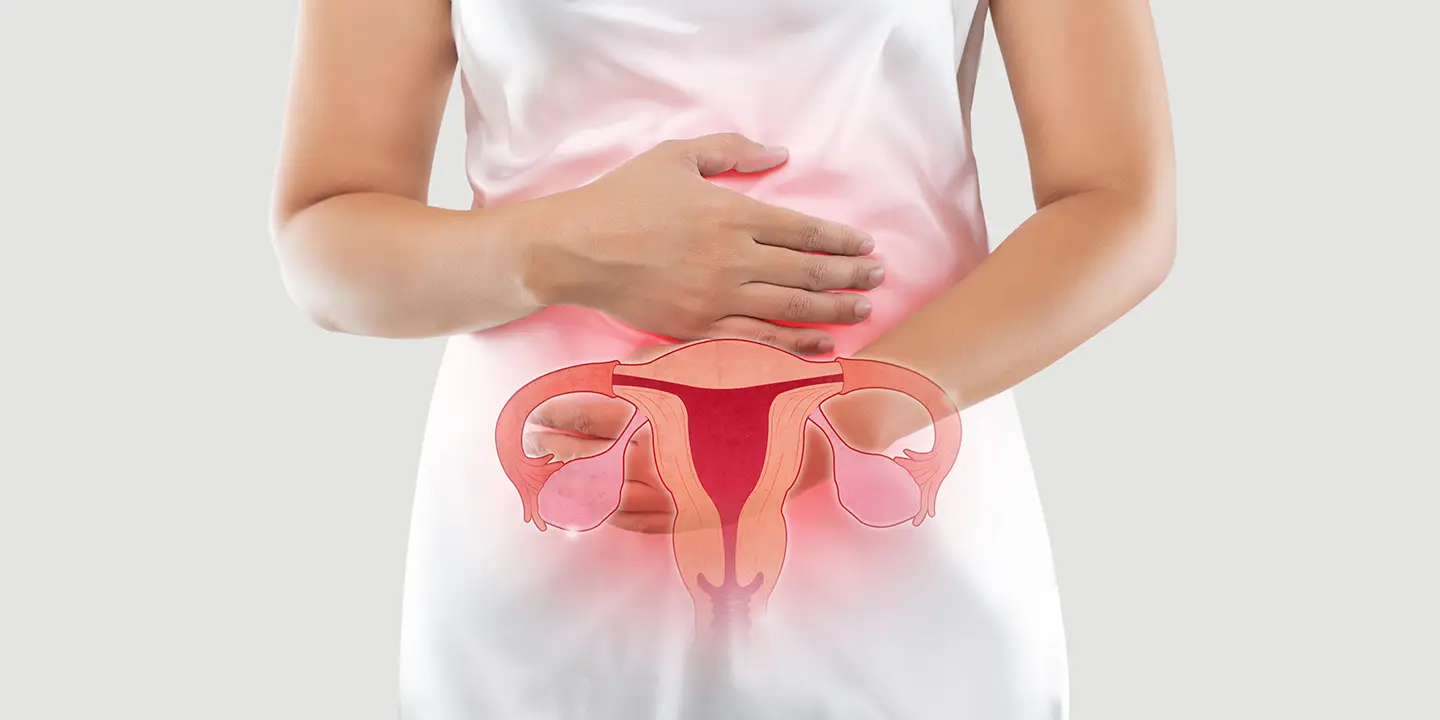
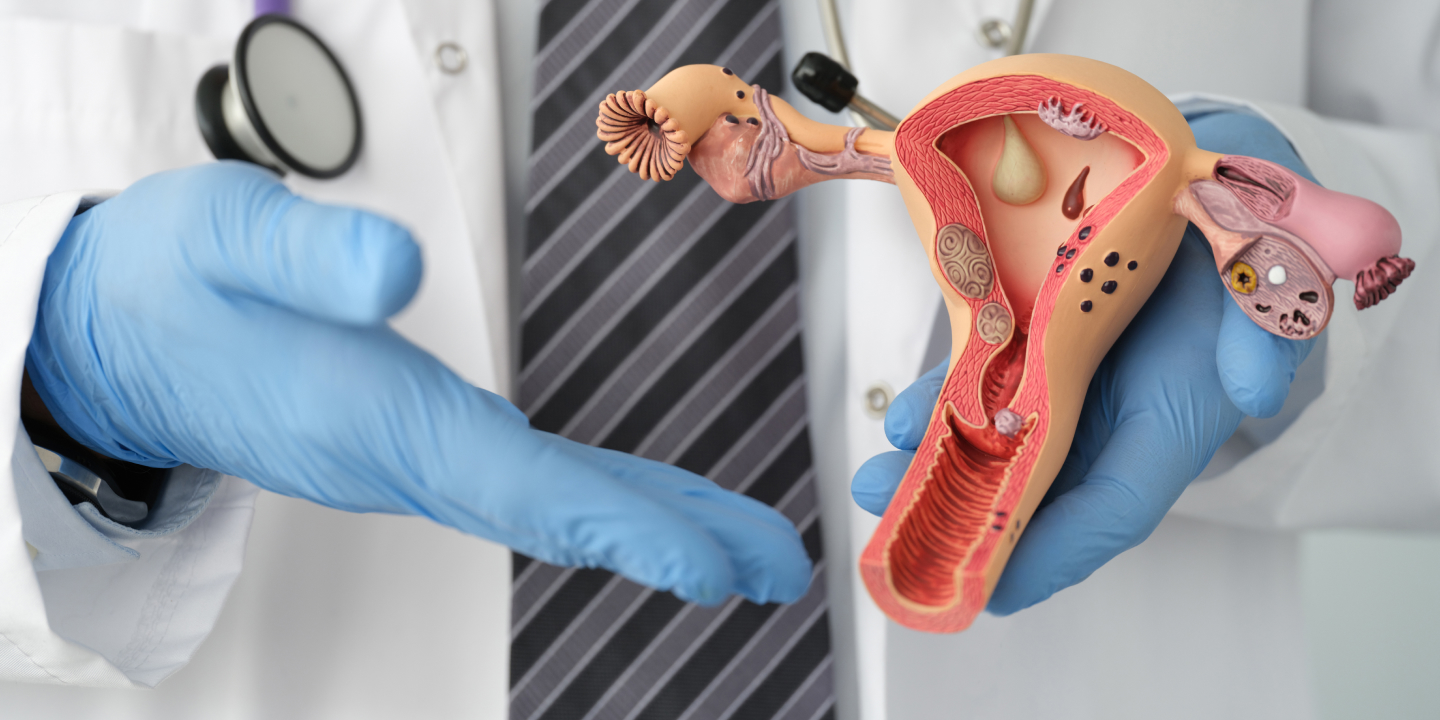
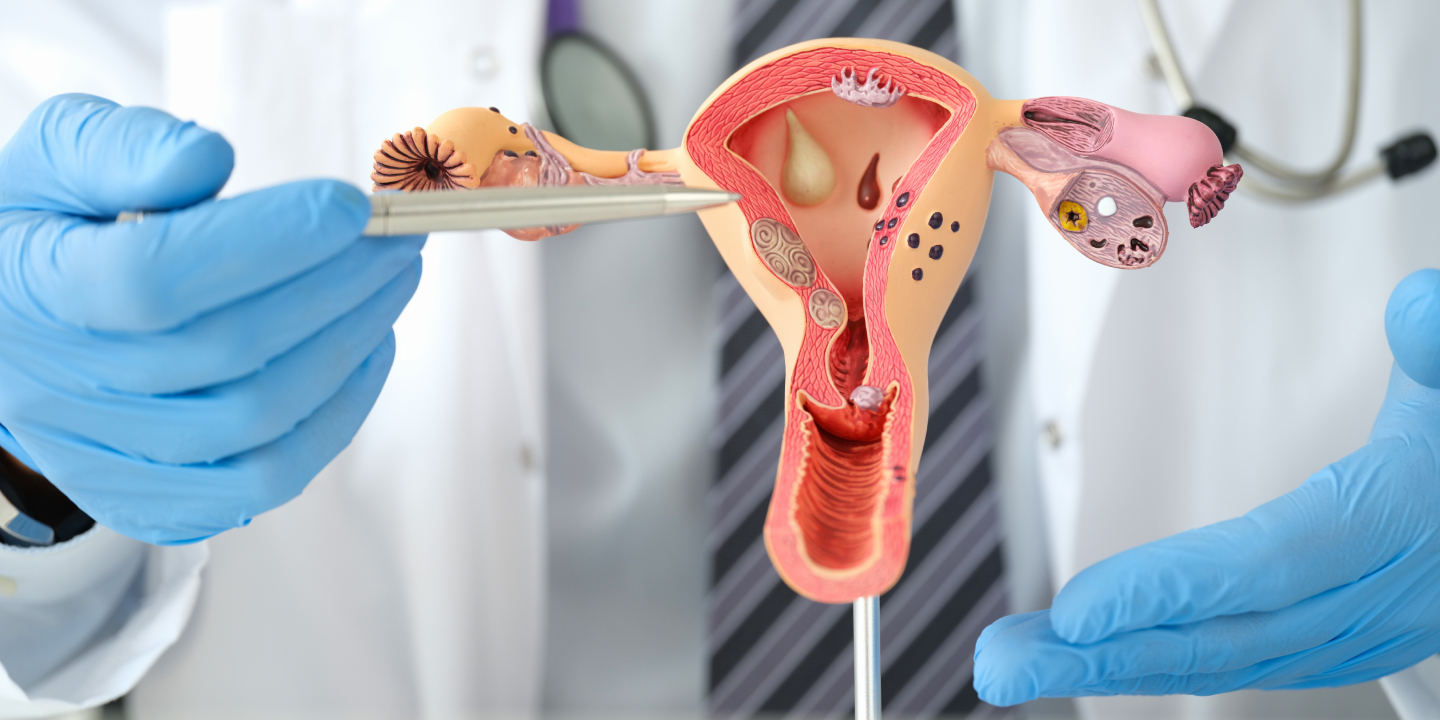
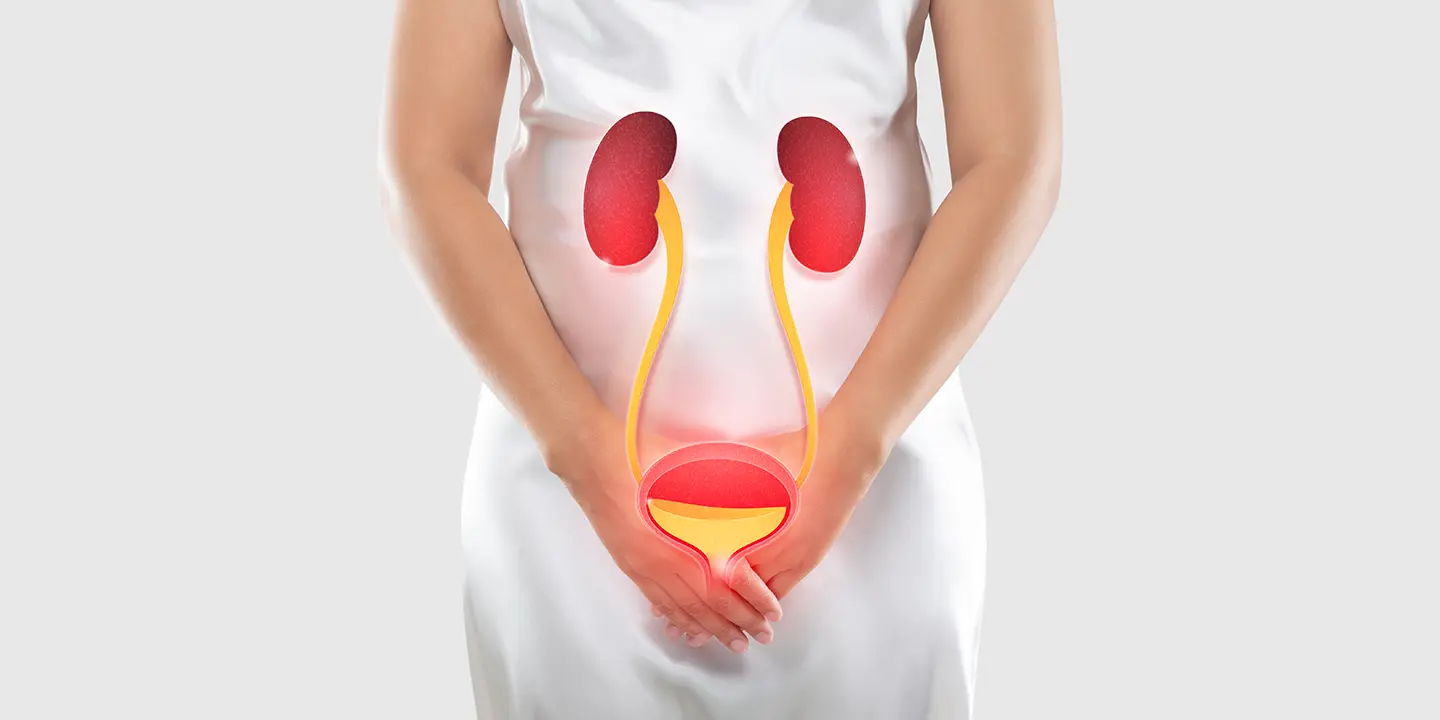
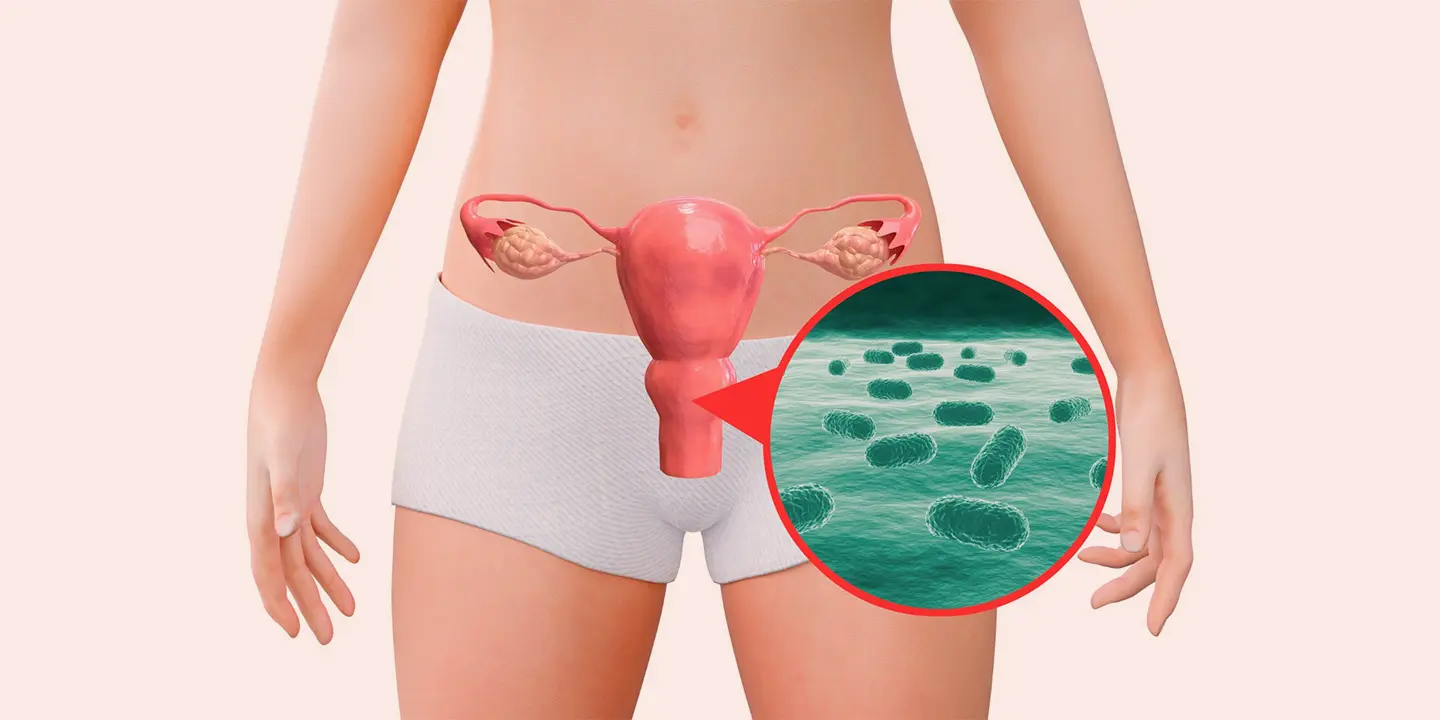
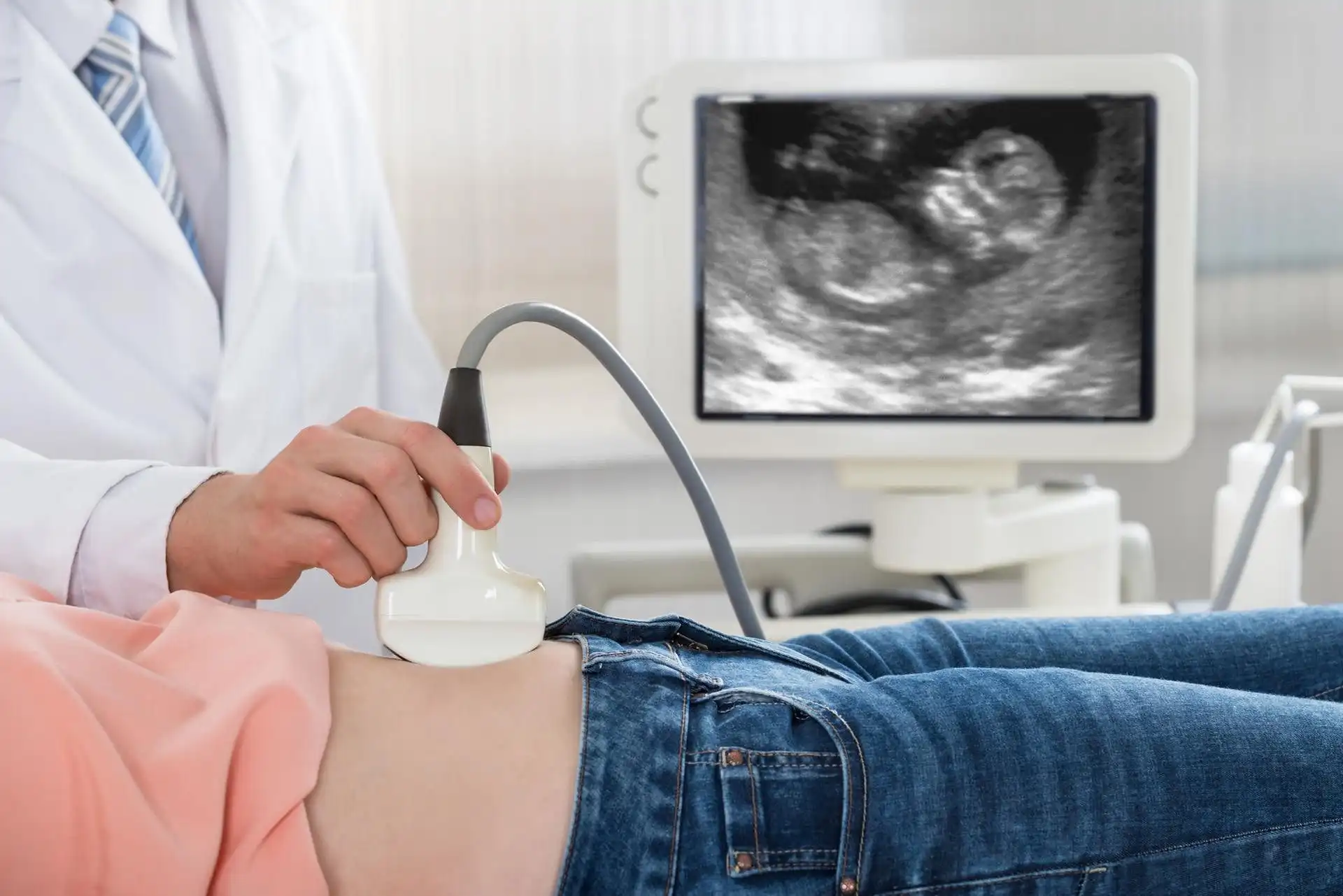
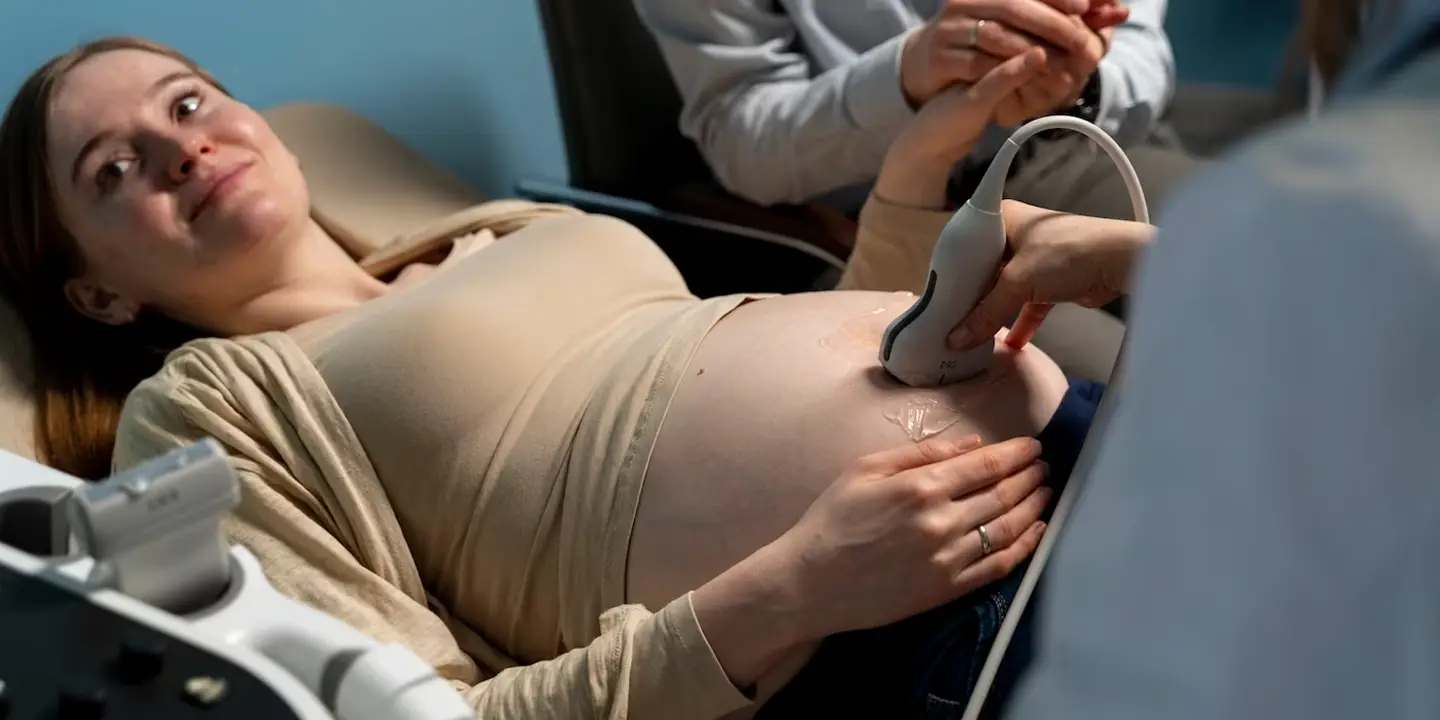
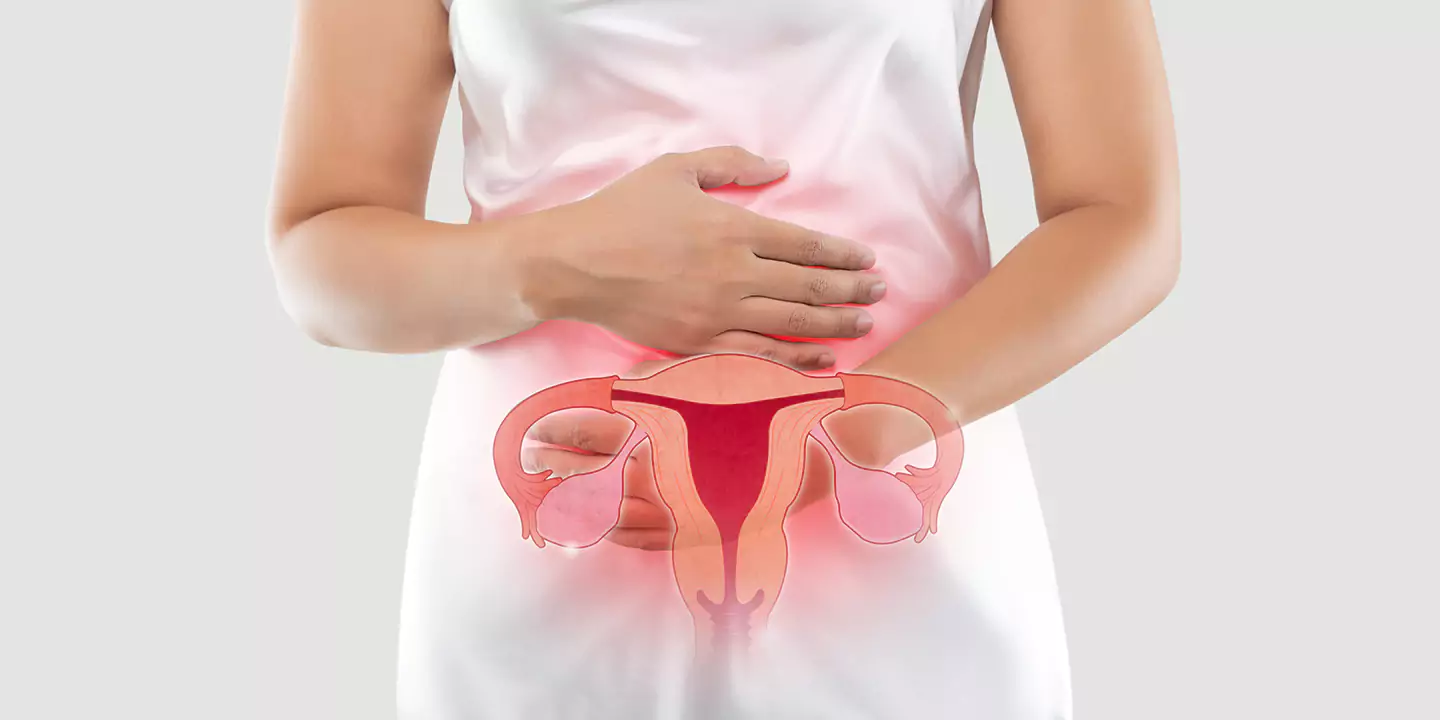
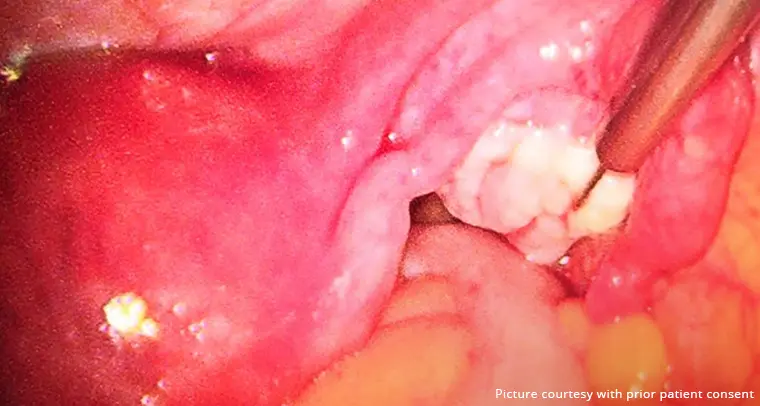
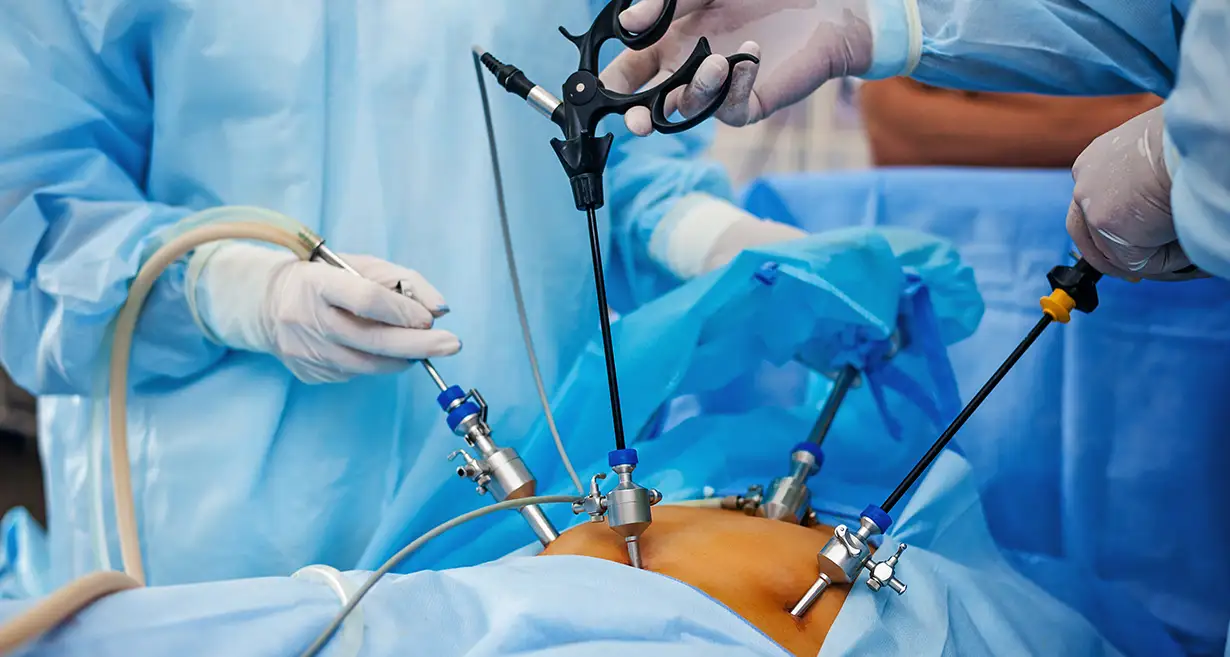
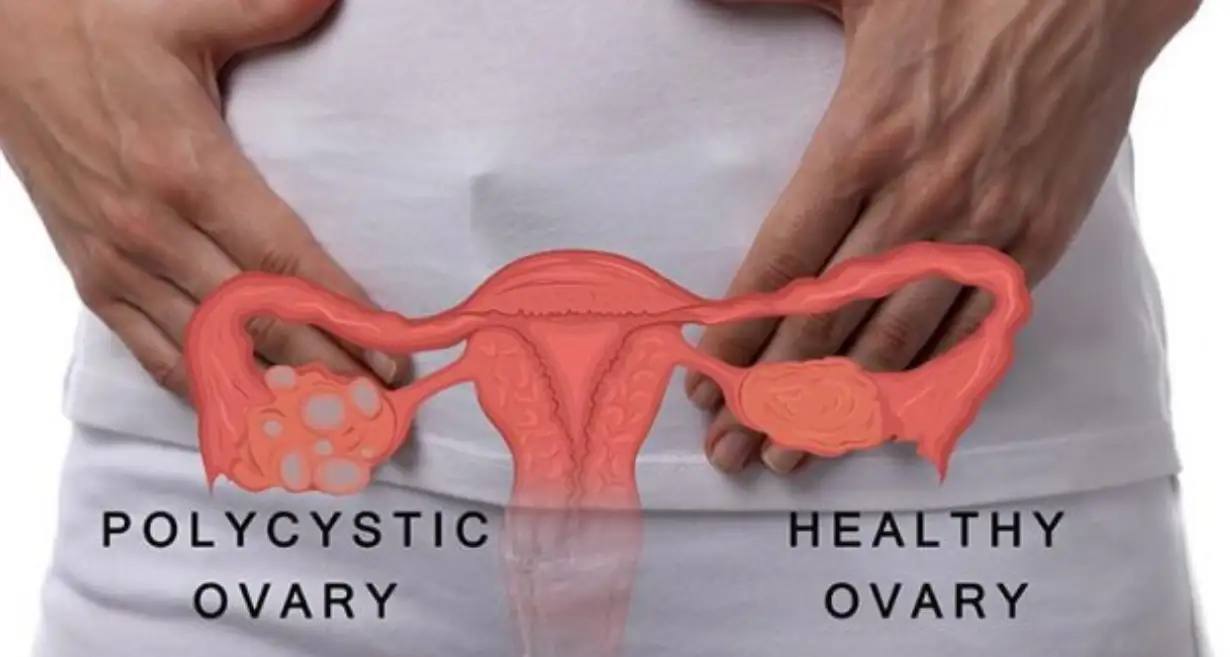
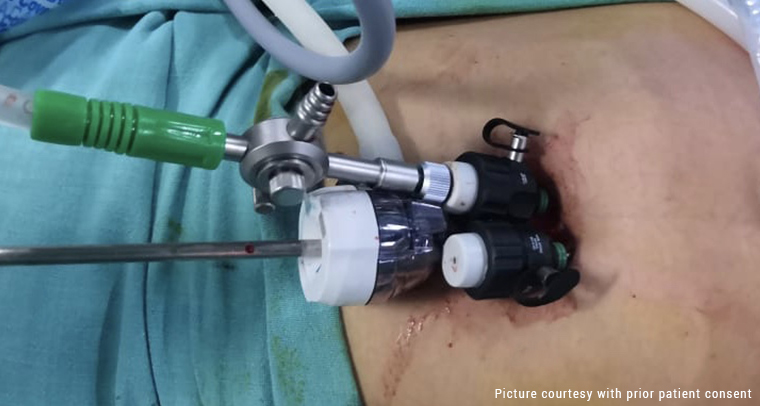
Ovarian cysts are sac-like outgrowths filled with fluid that may be located inside or outside the ovaries. They are usually formed during ovulation and are very common. In most cases, women do not experience any symptoms so, many patients discover ovarian cysts during a routine check-up involving ultrasound. As a result, most ovarian cyst cases pass undetected, and patients recover without any medical help.
Related Blog – Important Things Female and Teen Should Know About Ovarian Cysts
Do Ovarian Cysts Cause Infertility?
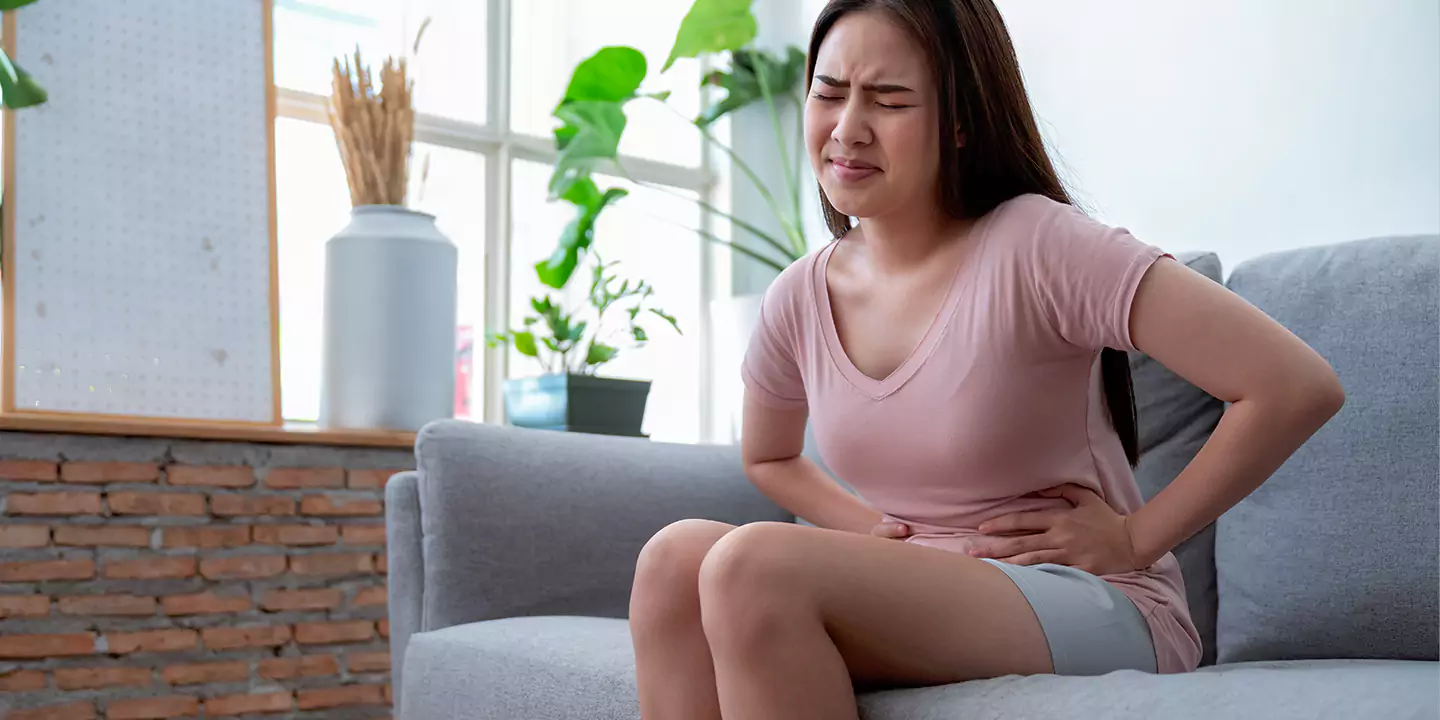
Ovarian cysts, when symptomatic, may cause abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, or fever. In such cases, the patient must visit a gynecologist, but it is rare. However, this lack of symptoms is also why prolonged ovarian cysts may unknowingly affect pregnancy or fertility. Not all ovarian cysts can cause infertility. There are a few types of ovarian cysts that may affect a patient’s fertility, which include:
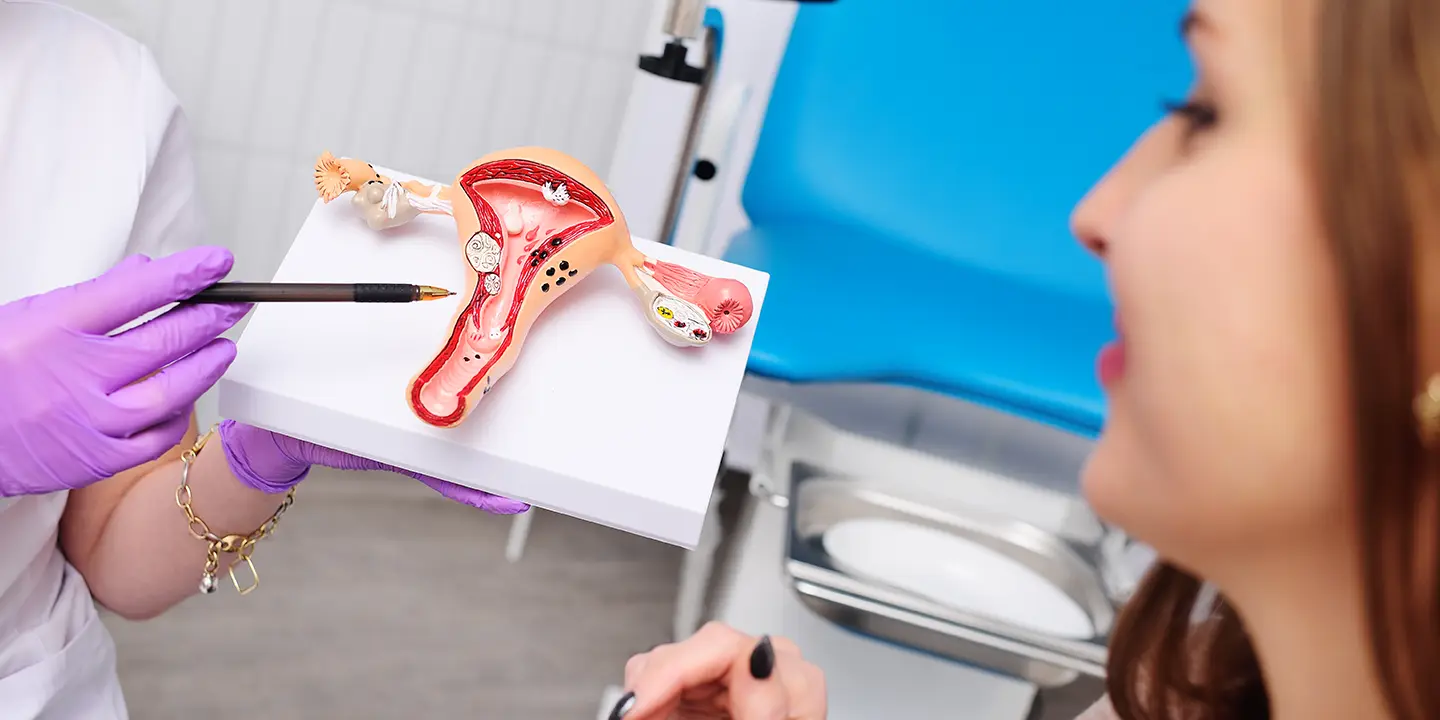
Endometriomas: Endometriosis, a condition in which the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of it, maybe the underlying cause of ovarian cysts. So, ovarian cysts formed due to endometriosis are called Endometriomas, and these may affect fertility and hinder natural pregnancy. 30–40% of endometriosis patients face infertility issues.
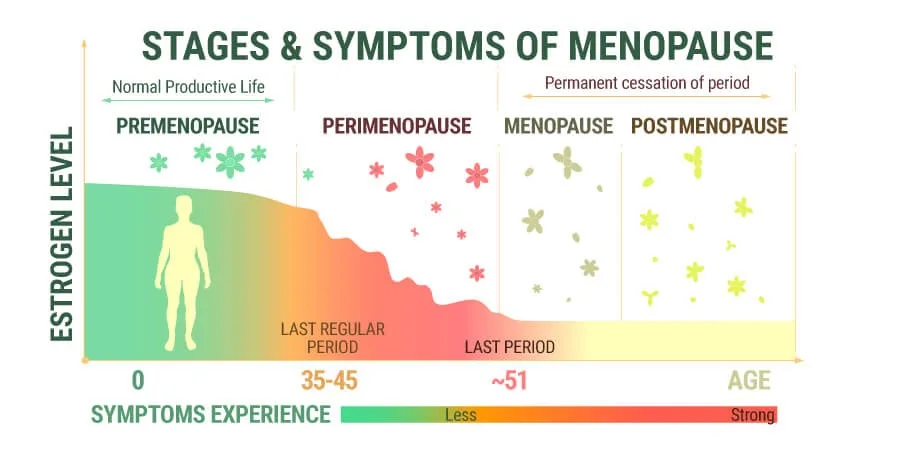
PCOS-related Ovarian cysts: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome induces the growth of many small pearl-sized cysts in the ovaries. They affect the menstrual cycles and cause hormonal disbalance. An abnormal hormone level in the body restricts the development of mature eggs, so they are not released from the ovaries. The body will not make progesterone in the absence of ovulation, which again causes hormonal disbalance and irregular menstrual cycles. If not treated, it may impact the chances of getting pregnant or lead to infertility at a later stage in life. Other cysts like Functional cysts, Cystadenomas, and Dermoid cysts are not associated with infertility at all.
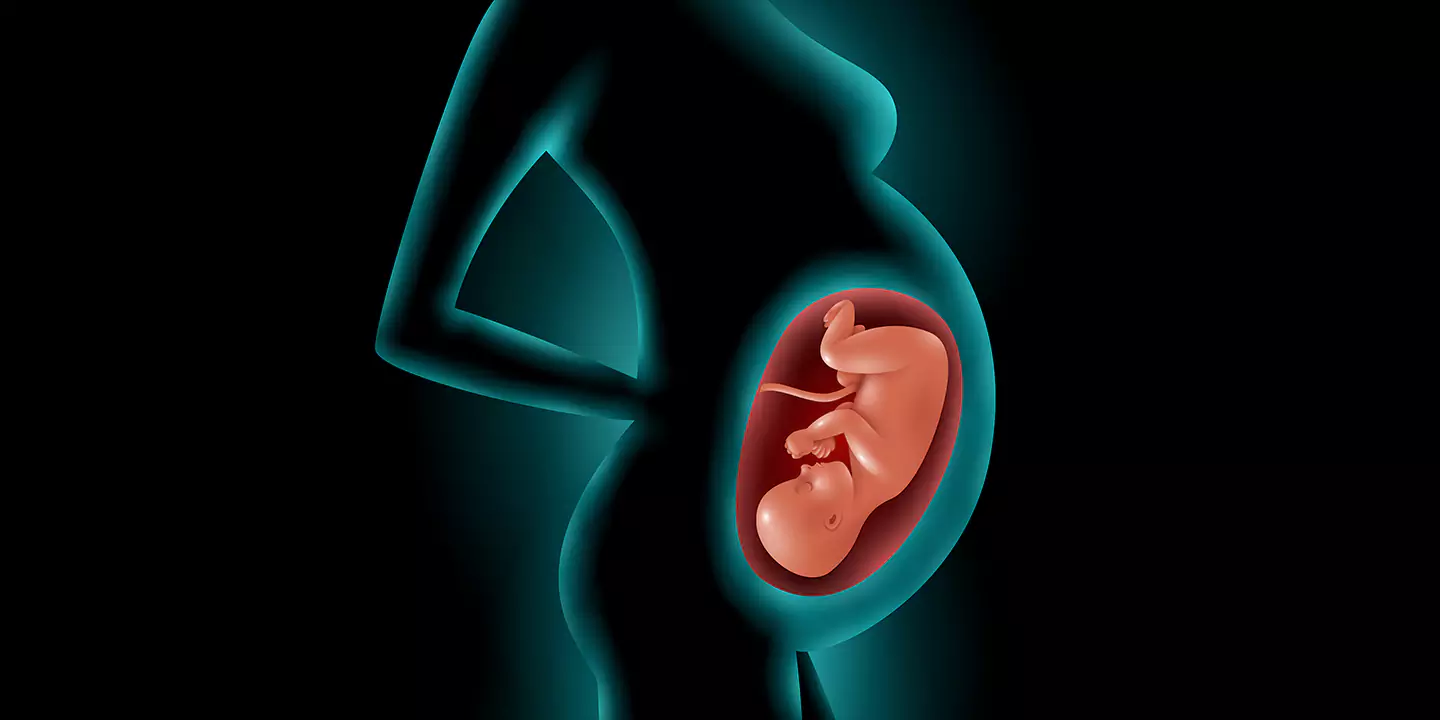
How Do Ovarian Cysts Impact Pregnancy?
Cysts may be present during pregnancy, but they are usually harmless. However, the situation may get sensitive if the cysts remain and grow throughout the pregnancy because there is a risk that the cyst may rupture during pregnancy, affecting childbirth. Also, sometimes, the continuous growth of the cyst may cause the ovary to turn into a painful position, causing ovarian torsion. In such cases, the patient must remain under constant medical supervision. Moreover, pregnant women with a history of PCOS are most likely to suffer from gestational diabetes, miscarriage, pregnancy-induced blood pressure, or premature childbirth. All these risk factors complicate the delivery process so, the birth must take place under the supervision of an experienced gynecologist in a controlled environment.
Related Blog – Genital Tuberculosis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Conclusion Ovarian cysts may not be the root cause of infertility or pregnancy complications, but if a woman cannot get pregnant naturally despite trying repeatedly, she must get herself tested. It is always wise to get a consultation because treating the cysts at an early stage will ensure that it does not lead to infertility or affect the pregnancy in the future.