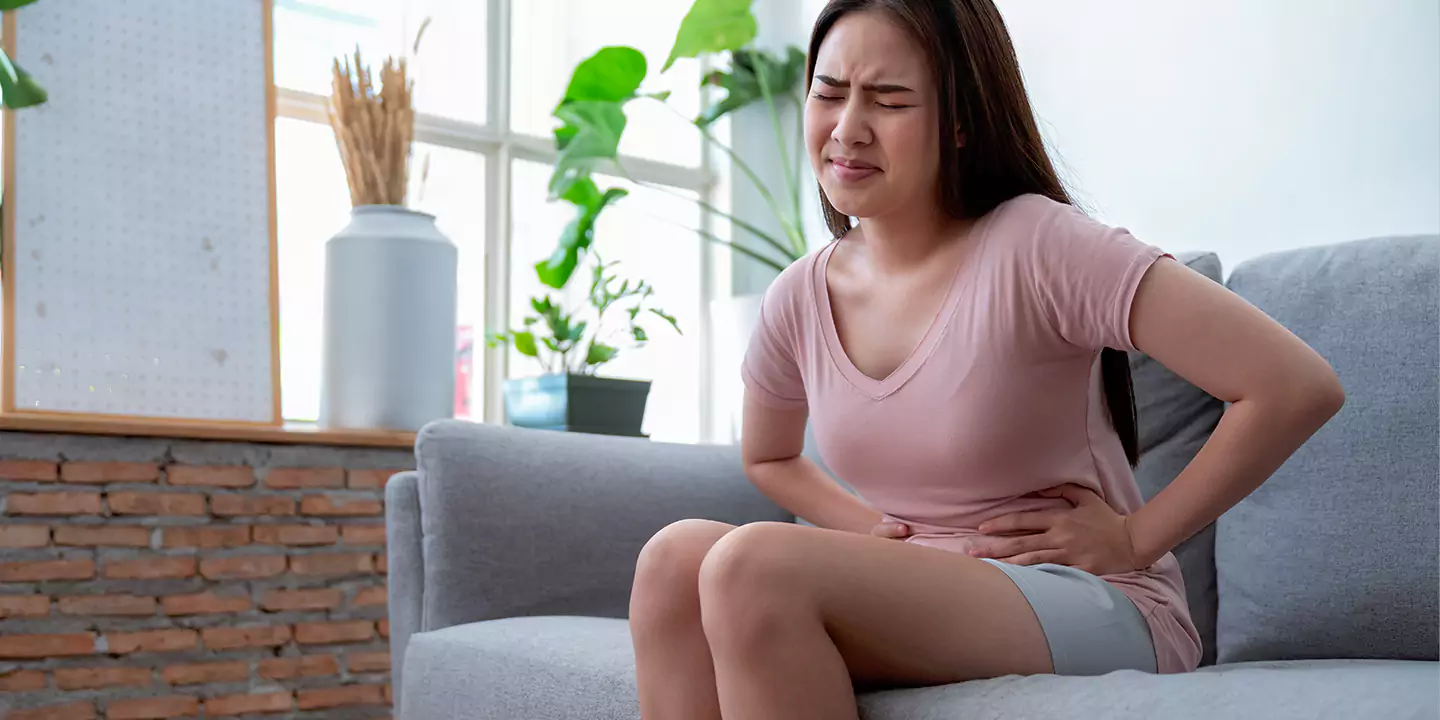
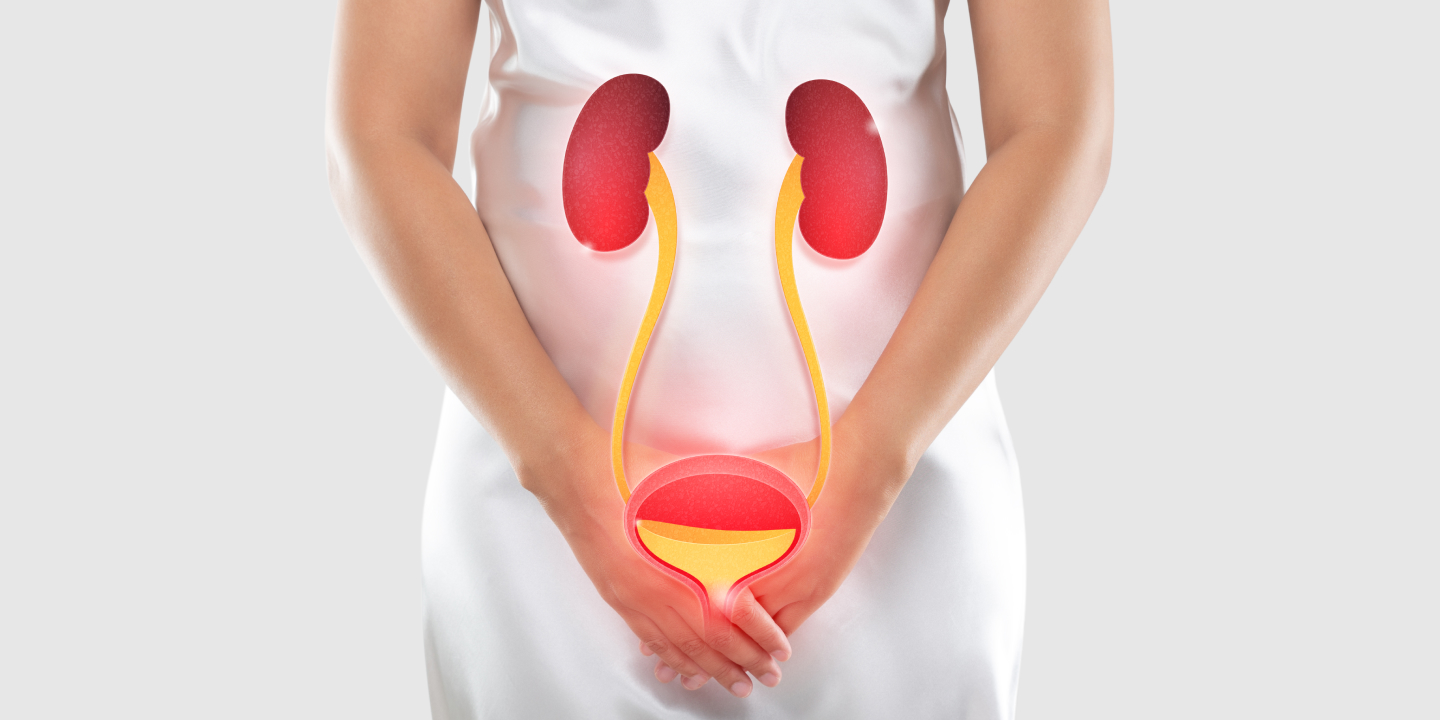
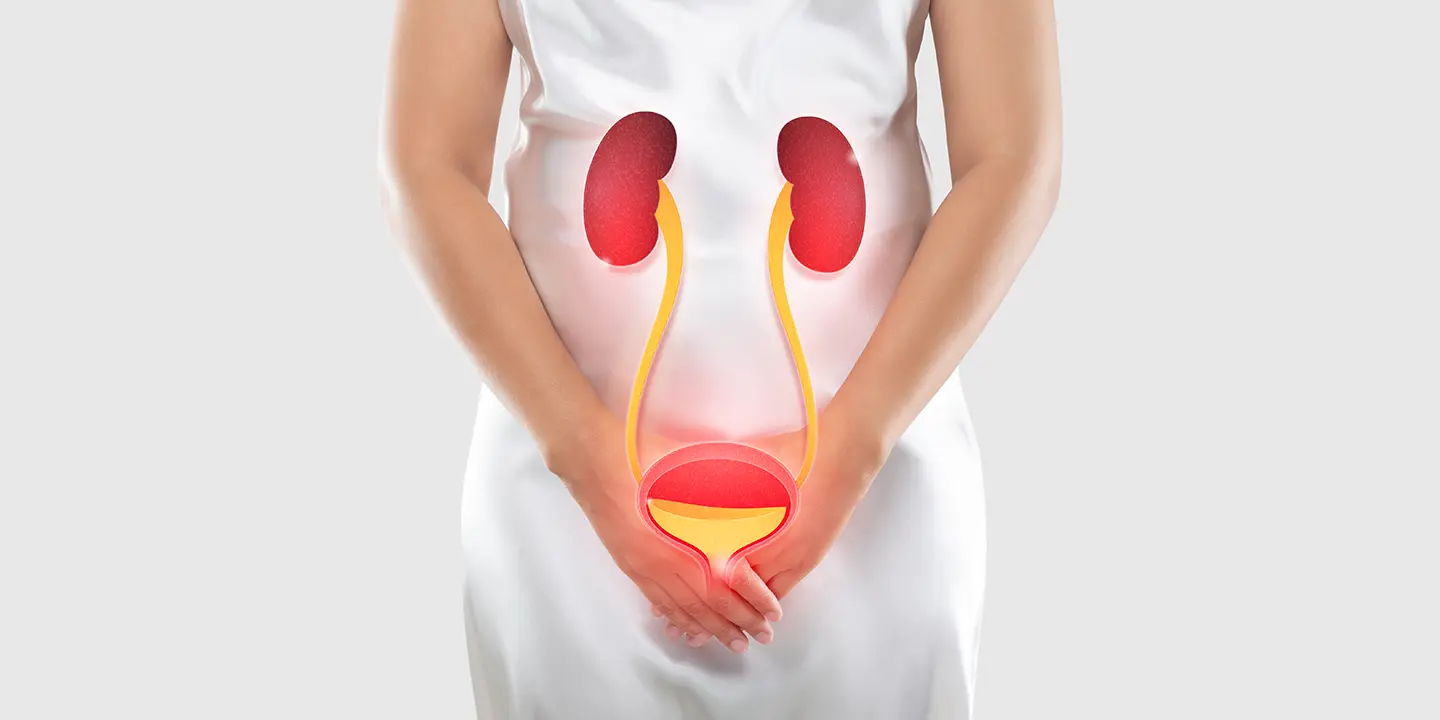
Among all the types of bacterial infection, urinary tract infection (UTI) accounts for the maximum load in the global population, affecting over 150 million people annually. UTIs are infections that occur in any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, etc.
Most UTIs occur in the lower urinary tract, causing pain, discomfort, and a burning sensation while you are urinating. The condition is more prevalent in women than in men and requires medical intervention for treatment and cure.
This article will explore everything there is to know about urinary tract infections, including their causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment.
In this Article
What is Urinary Tract Infection?
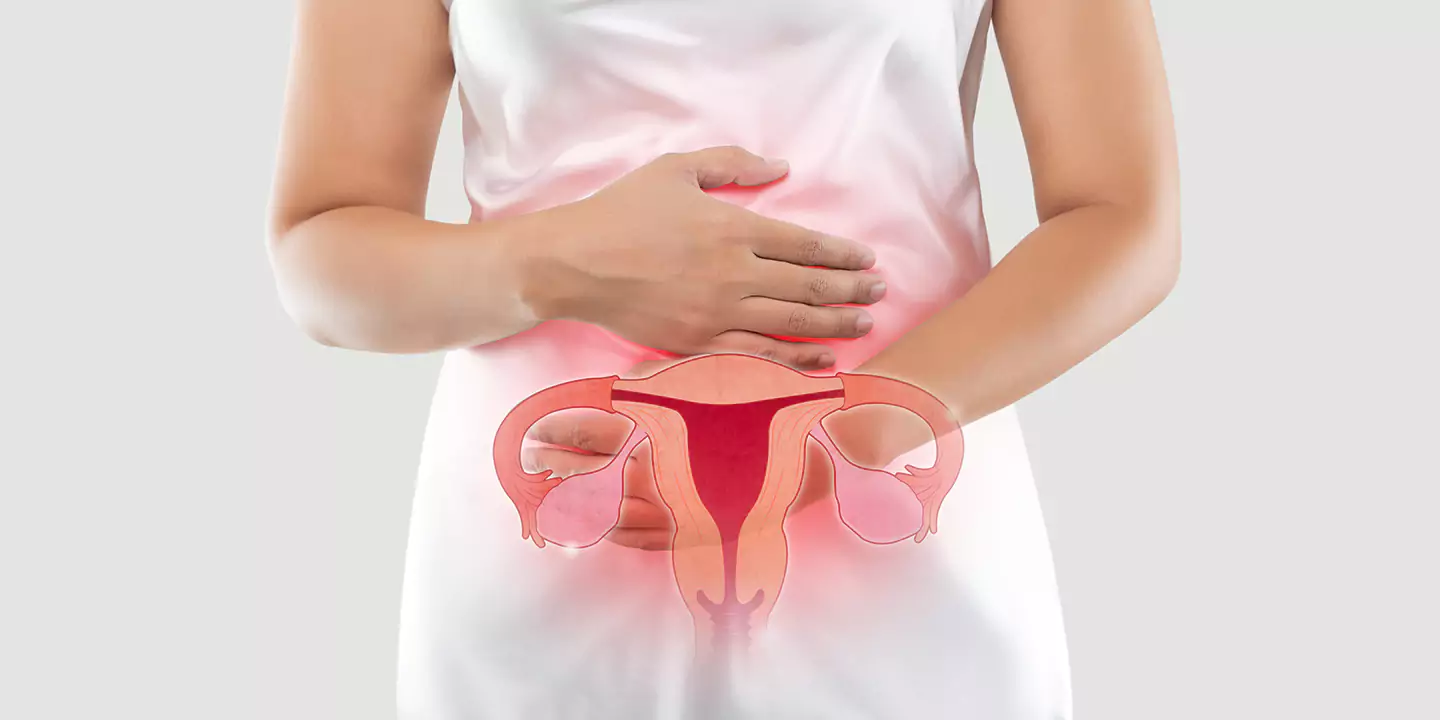
Urinary tract infection, commonly known as UTI, is a type of infection that occurs in the urinary system. It commonly affects the bladder and urethra but in severe cases can affect the kidneys as well.
Most (if not all) UTIs are caused by bacteria. In a few cases, UTIs are caused by fungi and viruses. The infection typically occurs when the urine that’s moving through the urinary system gets contaminated by microbes from the outside of the body, leading to infections and inflammation.
The condition is treatable and causes very prominent physical symptoms that should be taken seriously.
What are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection?
The urinary tract infection symptoms will depend on where the infection is. You have a set of standard symptoms and then you have a few specific symptoms worth taking notes on.
Let us start with the list of standard symptoms, which include:
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Urinating frequently but very less quantity
- Cloudy urine
- Red or bright pink colored urine
- Strong smell in the urine
- Pelvic pain
Besides these symptoms, there are a few subjective symptoms that occur depending on where the UTI is localized. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- If the UTI is in the kidneys, some of the common symptoms include pain in the back or side, high-grade fever, shaking and chills, nausea, and vomiting.
- If the UTI is in the bladder, some of the symptoms include pelvic pressure, discomfort in the lower belly, frequent and painful urination, and blood discharge in urine.
- If the UTI is in the urethra, some of the symptoms include discharge, and blood in the urine.
At Queen’s Gynecology, we often urge our patients to take these symptoms seriously and get the help they need before things take a turn for the worse.
What are the Causes of Urinary Tract Infections?
Women are more susceptible to UTIs than men due to the female anatomy. Hence, being aware of the symptoms and paying attention to the causes and risk factors can help prevent several women from experiencing this uncomfortable situation.
Before we discuss the causes of UTI, let us walk you through the potential risk factors:
Female anatomy – Shorter urethral length enhances the chances of infection.
Sexual activity – Engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse with a partner with an active infection or being sexually active with multiple partners.
Birth control – A few types of birth control can enhance the risks.
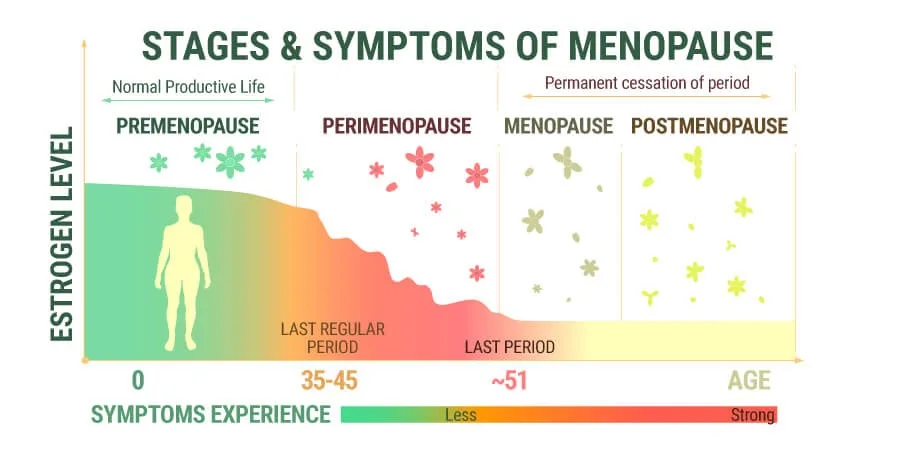
Menopause – A decline in estrogen levels during menopause change the chemistry of the urinary tract, leading to active UTIs.
With the risk factors out of the way, let us focus on the causes.
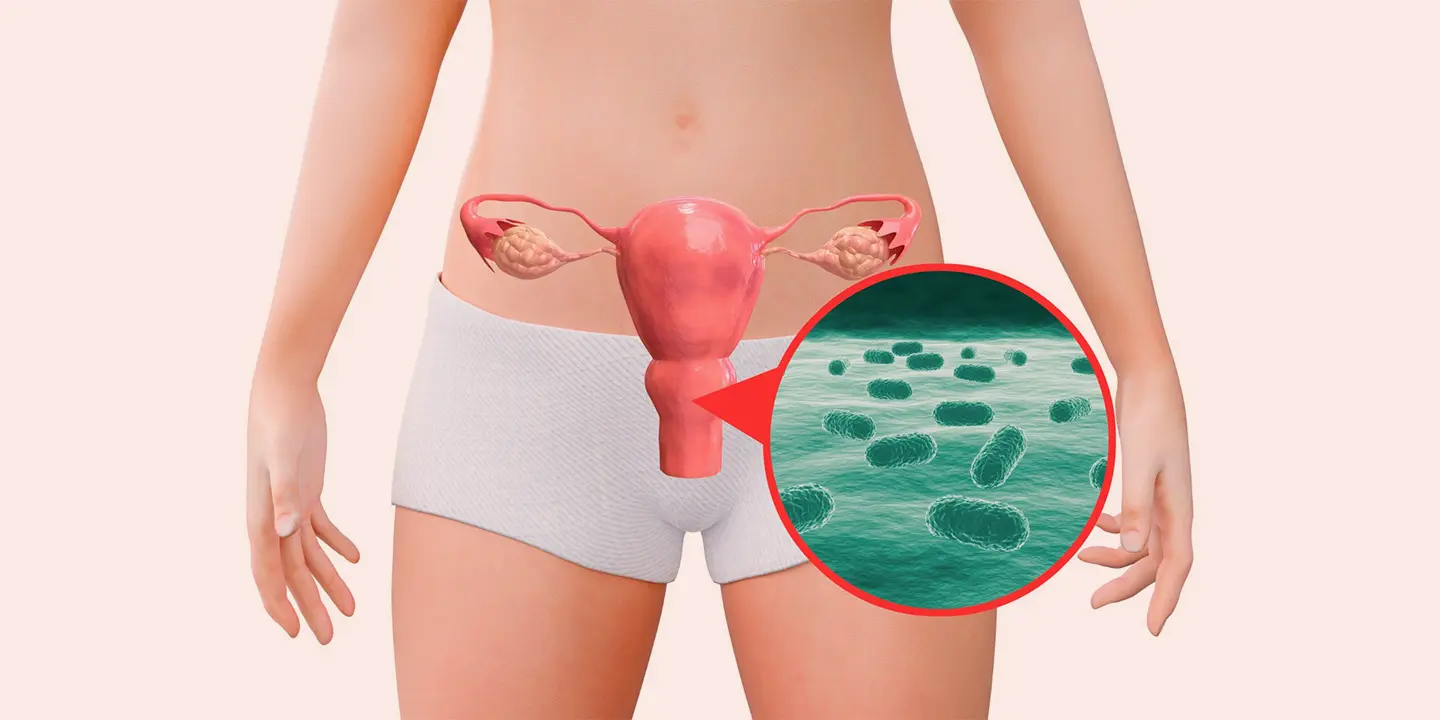
As we previously mentioned, UTIs are caused by microbes. For the most part, it is caused by bacteria but in rare cases, it could be due to fungus or viruses too. One of the most common types of bacteria that contribute to UTIs is E.coli.
In the case of urethral infection, it is typically due to sexually transmitted diseases, including herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma.
If you are experiencing any symptoms that you didn’t before, including burning sensation, pain, frequent urge to urinate, etc., it is a sign of an active UTI that needs immediate medical intervention. Don’t take the symptoms for granted.
How can Urinary Tract Infections be Treated?
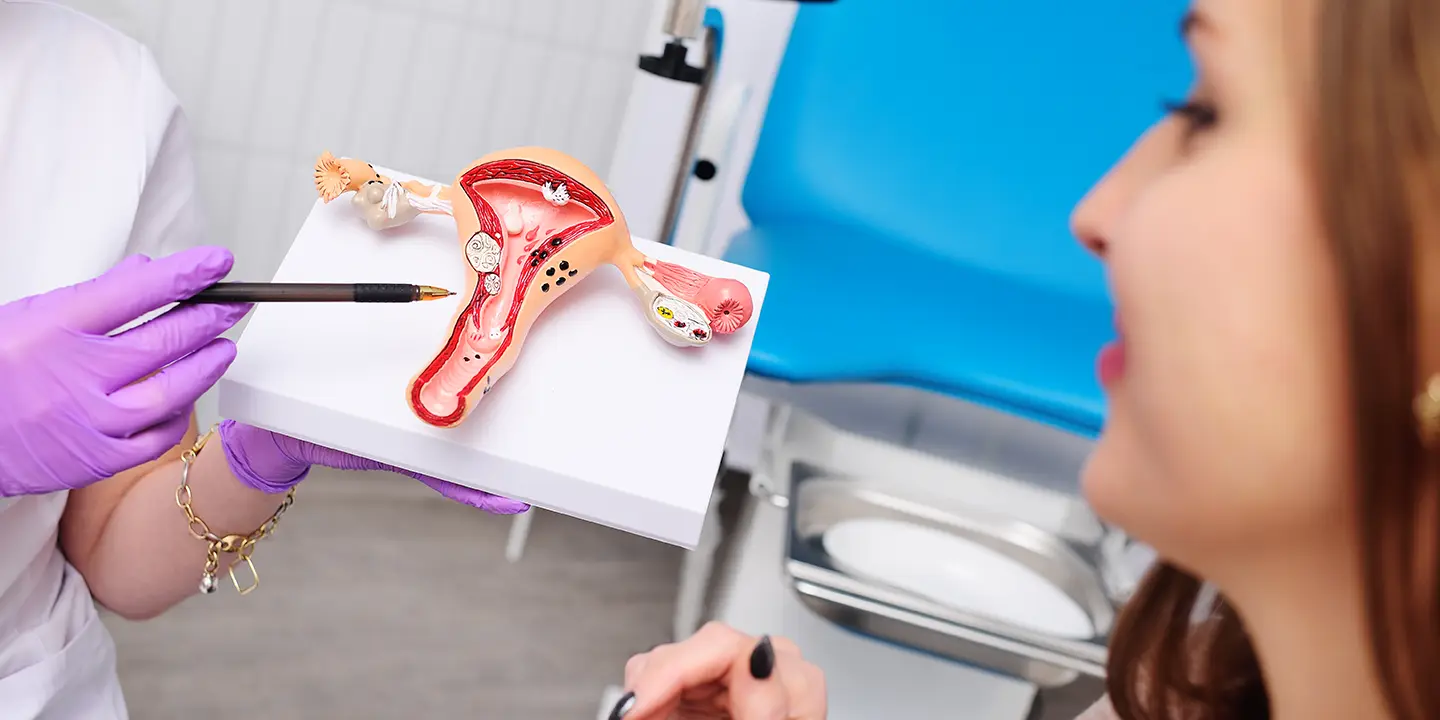
The treatment for a UTI starts with a comprehensive diagnosis. Identifying which kind of microbe is causing the infection is vital before starting the treatment.
Some of the most effective ways to diagnose a UTI are:
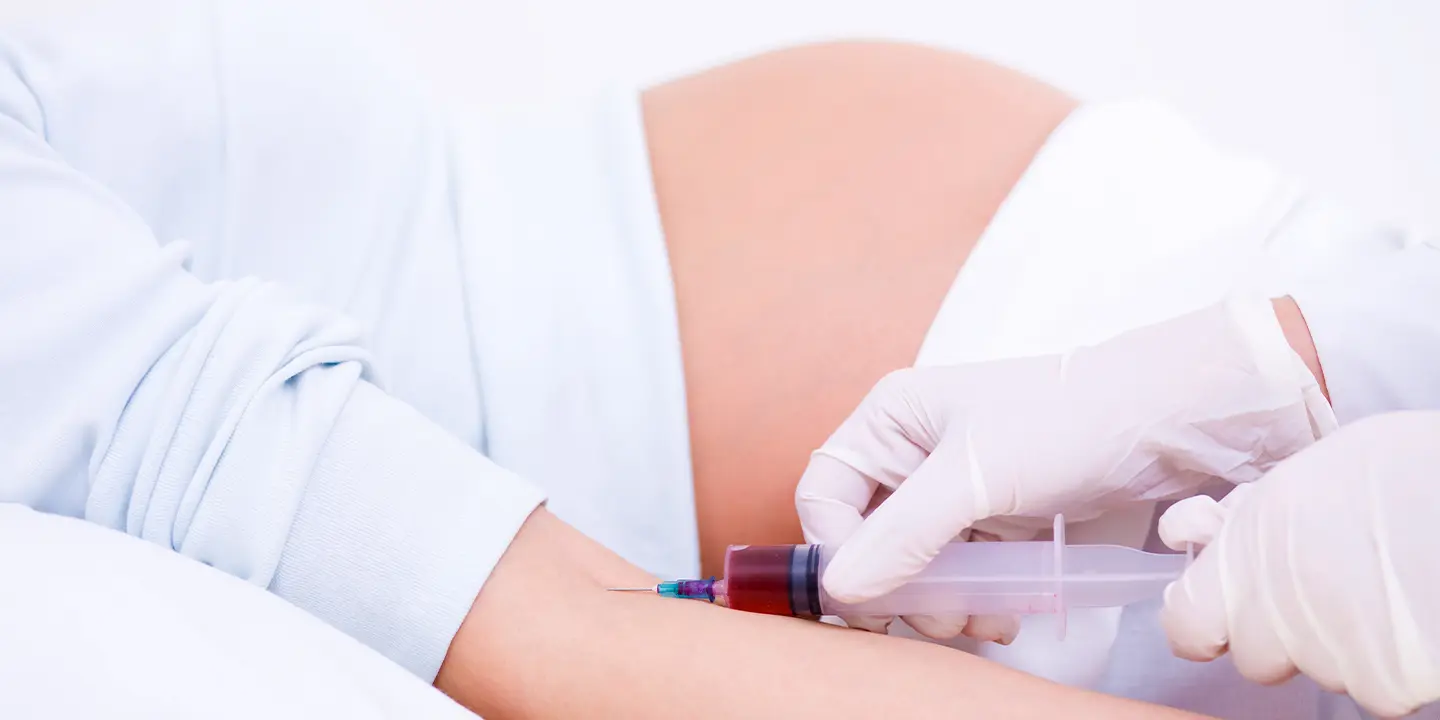
Urinalysis – Examines the urine sample for the presence of bacteria, and red and white blood cells to determine whether or not the patient has a UTI.
Urine culture – This determines the type of microbe (bacteria) that’s causing the infection.
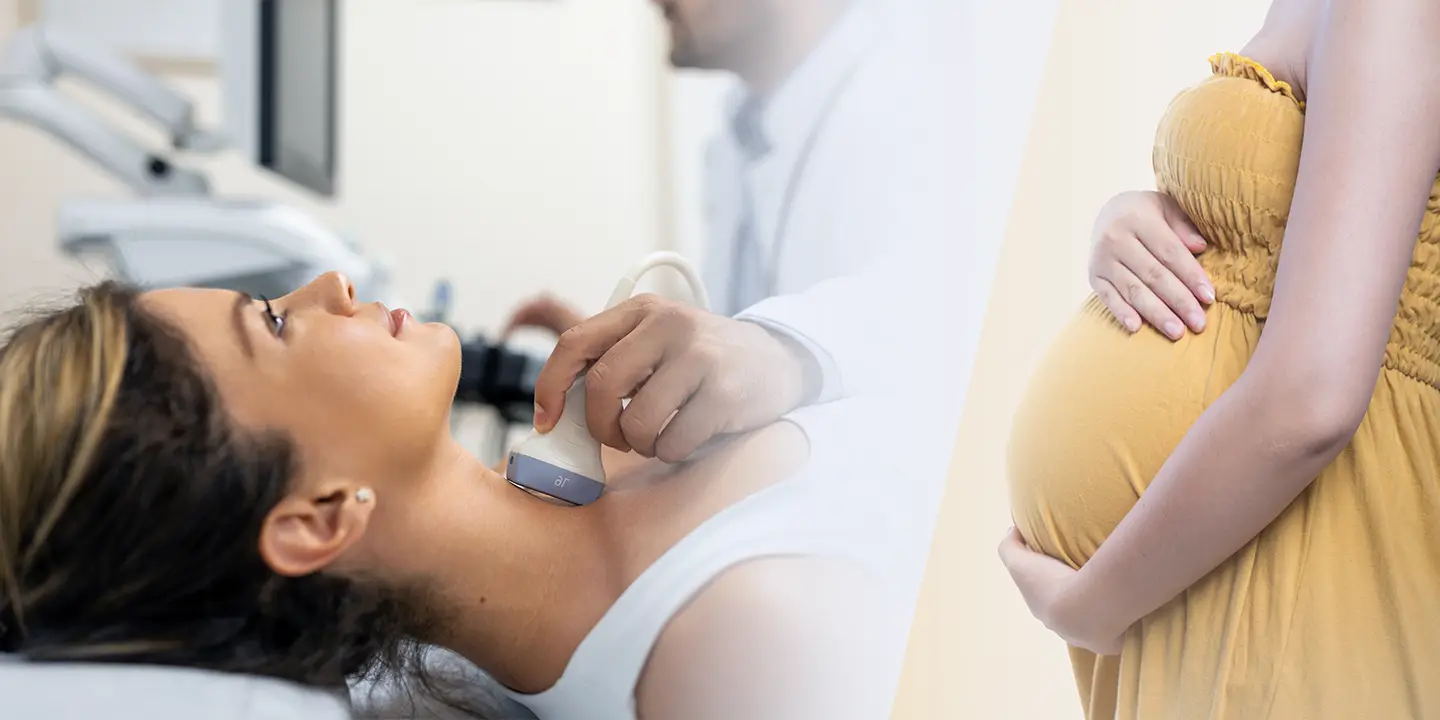
Imaging tests – CT scans and ultrasounds can help in identifying potential reasons why the infection is happening, especially if the doctor can’t pinpoint the exact reason from blood tests.
Cystoscopy – This is often kept as a last resort and uses a cystoscope to explore inside the bladder and urethra for blockages, signs of infections, etc.
Following a confirmed diagnosis, that’s when the treatment starts. The most common treatment for UTIs is antibiotics. The type and composition of the antibiotic will depend on the severity and the location of the infection.
Remember that antibiotics come with a prescribed course. So, if your doctor has prescribed it for two weeks, it is vital that you take the medicine for the urine infection in women for that duration even if the symptoms get better after the first week.
What are the Complications of UTI?
When treated optimally with medications, UTIs don’t normally lead to any drastic complications. However, issues arise when the condition is left untreated.
So, your work is to take the symptoms into account instead of brushing them to the side. Some of the most common complications include:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Permanent kidney damage
- Sepsis (in severe conditions)
- Delivering low-birth-weight infants
- Pre-term birth, etc.
Pay attention to the symptoms and if you feel uncomfortable and make you feel like you are in pain, it is always ideal to get the symptoms checked out by your gynecologist. Don’t take the symptoms for granted.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are painful and uncomfortable and they drastically affect one’s quality of life. If you suspect that you have an active infection from the symptoms, don’t hesitate from seeing a gynecologist. The idea that “waiting it out” will cure it is very wrong. The symptoms might get better but lack of treatment can lead to recurrent UTIs.
Prioritize seeing a gynecologist before it’s too late. Avail comprehensive examination and tailored treatment by the best team of doctors at Queen’s Gynecology. For more details, visit https://queensgynecology.in/contact-us.
FAQs
There is no conclusive research that backs the claim of cranberry juice is an effective option for UTI prevention. However, more research is being conducted on the subject.
Maintaining good personal hygiene is key to preventing UTIs. Besides that, you should also maintain optimal hygiene when engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse.
When asked to list five bacteria that can cause urinary tract infection, the most common ones are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.