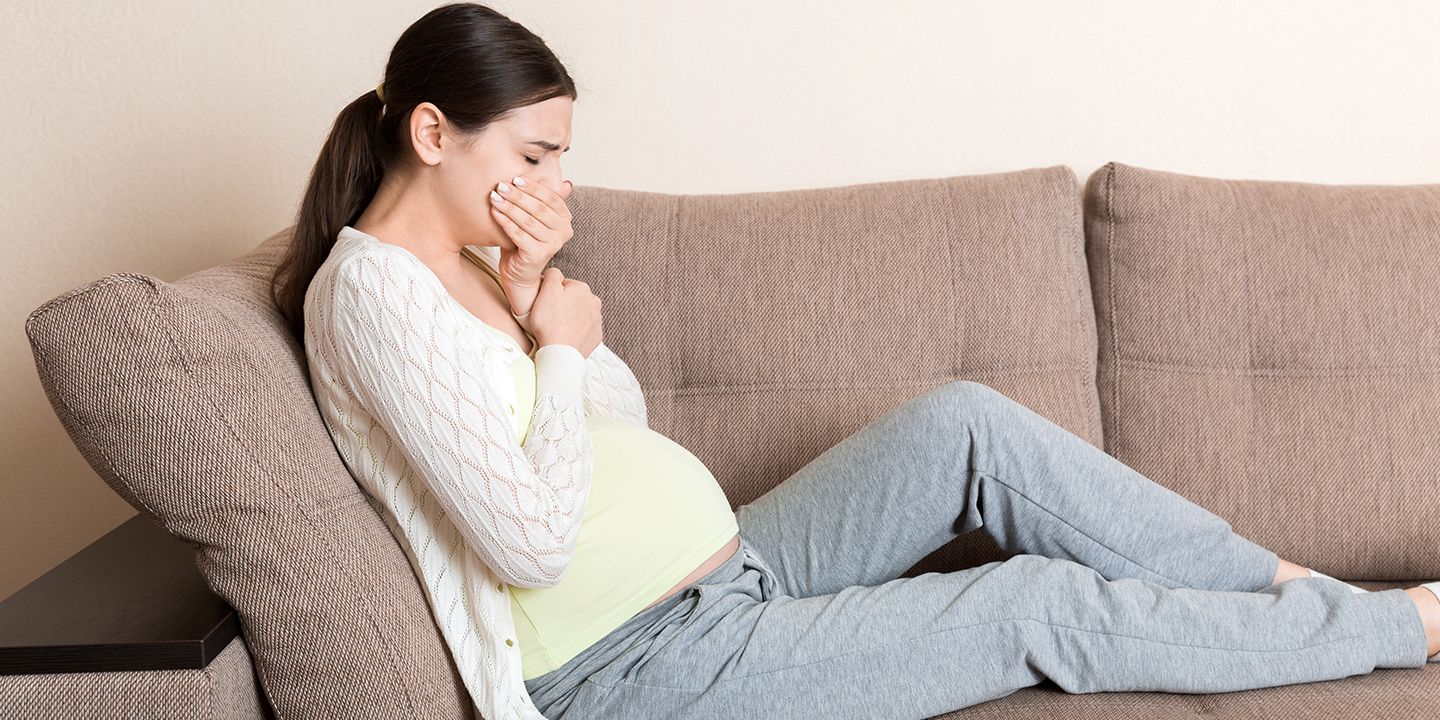
Breathing problem during pregnancy can catch many expectant mothers off guard. From subtle changes to noticeable challenges, the simple act of taking a deep breath can suddenly feel different. These alterations in breathing patterns often accompany the various stages of pregnancy, impacting routine activities and moments of relaxation. Addressing these challenges is crucial not only for the comfort of the expecting mother but also for ensuring a healthy journey for both her and the developing baby.
Read More in Hindi:- Am I Pregnant? 10 Early Pregnancy Signs and Symptoms
In this guide, we aim to explore these common but often overlooked aspects of pregnancy, offering practical insights and solutions to help navigate and manage breathing difficulties effectively.
In this Article
- 1 Understanding Common Respiratory Issues in Pregnancy
- 2 Breathing Problems in the First Trimester
- 3 Breathing Problems in the Second Semester
- 4 Breathing Problems in the Third Semester
- 5 Risk Factors and Complications
- 6 Potential Complications
- 7 Tips and Techniques for Relief
- 8 Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
- 9 Medical Interventions and Treatments
- 10 Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
- 11 Obstetric Care and Delivery Planning
- 12 Why Choose Queen’s Gynaecology?
Understanding Common Respiratory Issues in Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings a whirlwind of changes, and while it’s a beautiful phase, it also introduces various adjustments in a woman’s body, including those affecting the respiratory system. Understanding the common respiratory issues encountered during pregnancy sets the groundwork for effectively addressing these challenges.
Dyspnea (Shortness of Breath)
One of the most prevalent respiratory issues experienced by expectant mothers is dyspnea or shortness of breath. This sensation often intensifies in the second and third trimesters, especially during physical exertion or when lying down.
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation, characterized by rapid or deep breathing, can occur due to heightened anxiety or increased demand for oxygen. Pregnancy-induced hormonal changes may trigger this response, leading to episodes of rapid breathing that can be distressing but are typically not harmful.
Asthma
For individuals with a history of asthma, pregnancy can influence the condition. While some experience improved symptoms, others might face exacerbations due to hormonal fluctuations or environmental triggers.
Rhinitis (Nasal Congestion)
Rhinitis, marked by nasal congestion or a runny nose, is a common occurrence during pregnancy. Hormonal changes can cause the nasal passages to swell, leading to breathing difficulties or discomfort, particularly in the first trimester.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea, characterized by disrupted breathing during sleep due to narrowed or obstructed airways, might worsen breathing during pregnancy.
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
Pregnant individuals are more susceptible to upper respiratory tract infections, such as the common cold or flu. These infections can lead to nasal congestion, coughing, sore throat, and difficulty breathing, adding to the respiratory challenges during pregnancy.
Breathing Problems in the First Trimester
Causes of Breathing Problems
During the first trimester, breathing difficulties in pregnancy may primarily arise due to hormonal changes and increased progesterone levels.
These hormonal shifts can impact the respiratory system, causing breathlessness during first trimester. Causes may include:
- Increased Oxygen Demand: The growing embryo requires more oxygen, prompting the body to adapt by altering breathing patterns.
- Elevated Metabolic Rate: As the body works harder to support the developing fetus, the metabolic rate rises, necessitating increased oxygen intake.
- Nasal Congestion: Hormonal changes can lead to swelling in the nasal passages, causing congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Morning Sickness: Nausea and vomiting can also contribute to breathing issues by limiting airflow.
Breathing Problems in the Second Semester
Causes of Breathing Problems
The second trimester is often considered the most comfortable period for most pregnant women. Breathlessness during 2nd trimester might persist due to:
- Uterine Expansion: The enlarging uterus puts pressure on the diaphragm, reducing lung capacity and causing shortness of breath.
- Weight Gain: Increased body weight can affect lung function and make breathing feel more labored.
- Heart Rate Changes: The heart pumps more blood to meet the demands of the developing baby, affecting respiratory rates.
- Muscle Strain: Growing abdominal muscles may strain chest muscles, influencing breathing patterns.
Breathing Problems in the Third Semester
Causes of Breathing Problems
Breathless during third trimester may intensify due to:
- Fetal Growth: The baby’s growth occupies more space, pressing against the diaphragm and restricting lung expansion.
- Progesterone Levels: Continual elevation of progesterone may further impact breathing as the pregnancy progresses.
- Edema: Swelling in the feet and ankles can also extend to the lungs, making breathing more challenging.
- Position of the Baby: The baby’s position can impact the mother’s lung capacity by compressing the diaphragm or pushing against the ribcage.
Throughout pregnancy, it’s essential to monitor any significant or persistent breathing difficulties and consult healthcare professionals for proper evaluation and guidance.
Risk Factors and Complications
Identifying High-Risk Cases
During pregnancy, while many breathing issues are part of the natural course, certain scenarios warrant closer attention.
Keep an eye out for the following situations that might indicate a more serious concern:
- Persistent Shortness of Breath: If you find yourself constantly struggling for air even during moments of rest, this could signify an underlying problem.
- Severe Chest Pain or Tightness: Experiencing intense discomfort or pressure in the chest that doesn’t alleviate with rest warrants immediate attention.
- Rapid Heart Rate: A consistently elevated heart rate, especially without exertion, should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Potential Complications
Persistent or severe breathing difficulties, if left unaddressed, might lead to potential complications, although rarely.
Some associated risks include:
- Increased Risk of Preeclampsia: Severe shortness of breath can sometimes be an indicator of this pregnancy-related condition characterized by high blood pressure.
- Impact on Fetal Health: In extreme cases, inadequate oxygen intake might affect the baby’s growth and development.
- Exacerbation of Underlying Conditions: Pre-existing conditions like asthma might worsen, necessitating careful management to ensure both maternal and fetal well-being.
Tips and Techniques for Relief
During pregnancy, managing breathing challenges involves adopting simple yet effective strategies that promote comfort and ease.
- Pacing Activities: Break tasks into smaller, manageable segments to prevent overexertion and breathlessness.
- Proper Posture: Maintain an upright posture while sitting or standing to allow the lungs more room for expansion.
- Pillow Support: Use pillows while sleeping to elevate your upper body slightly, reducing pressure on the diaphragm.
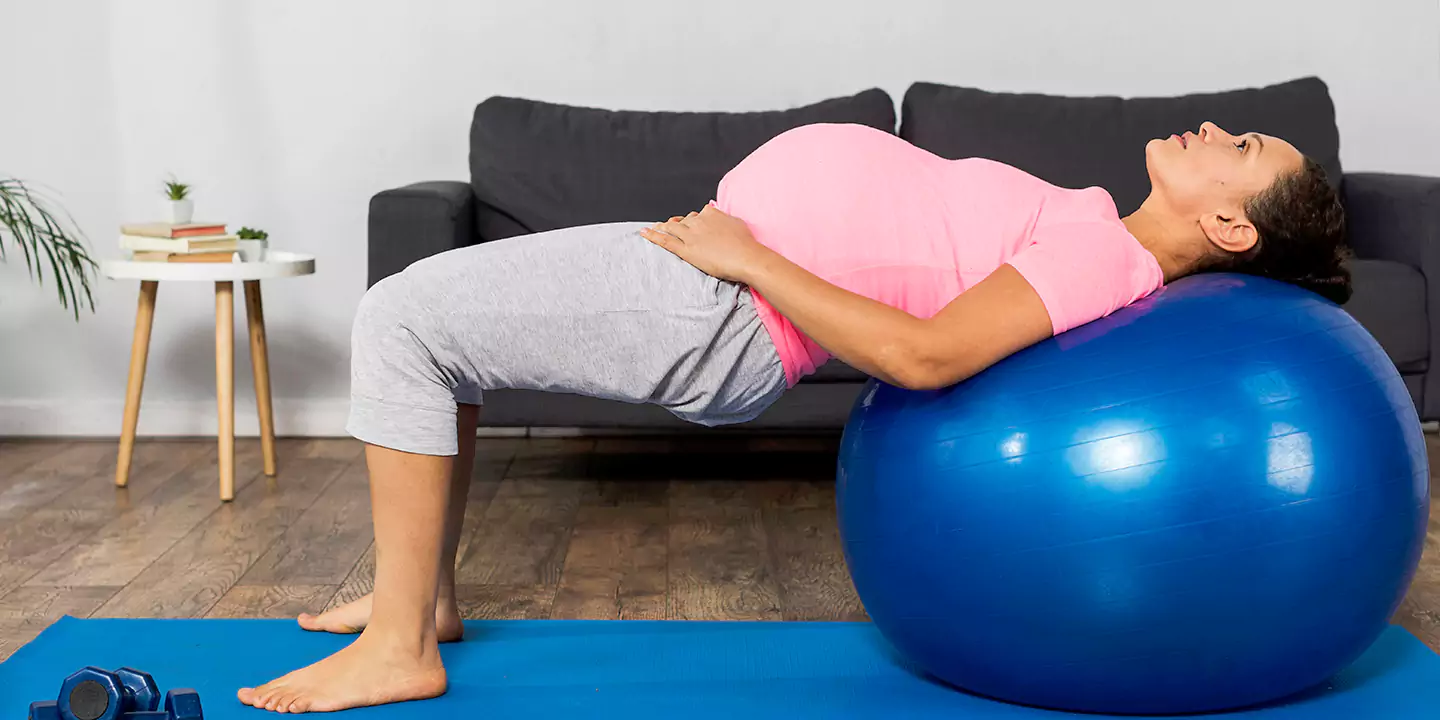
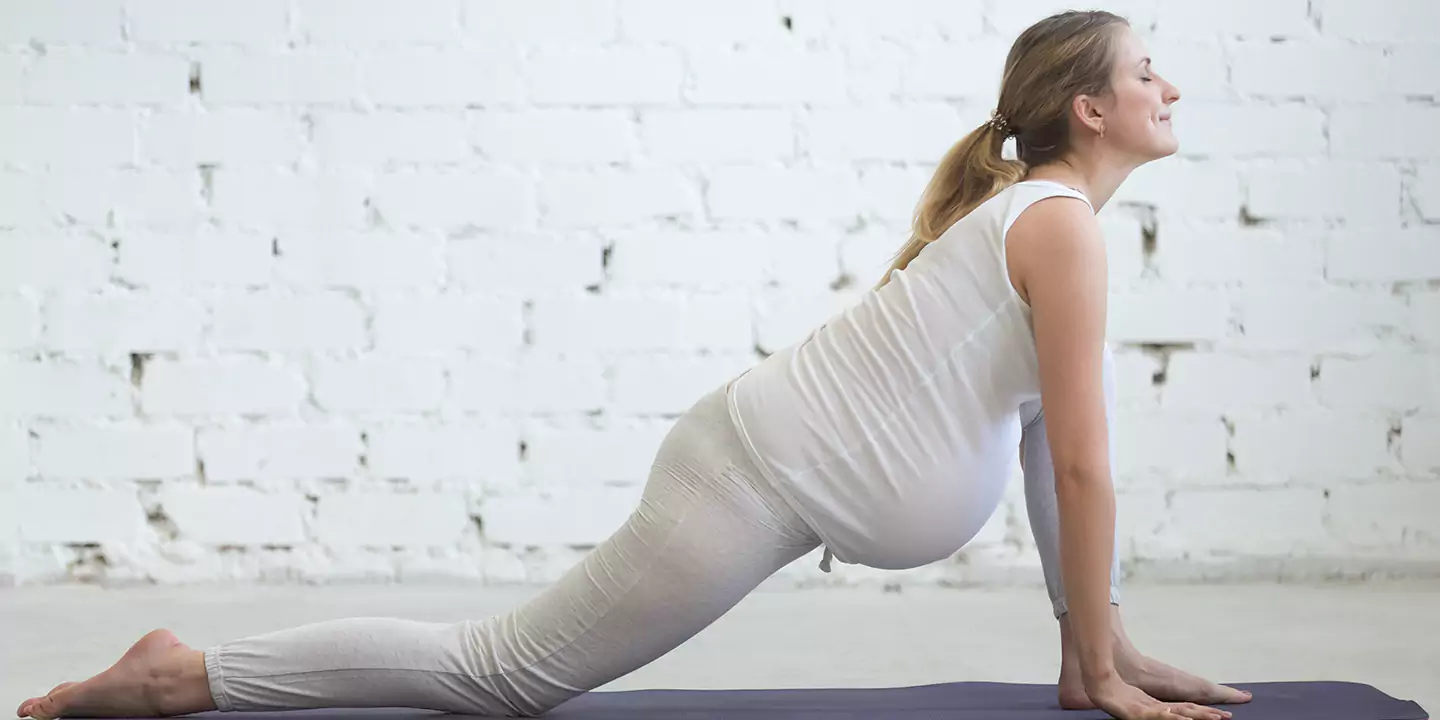
- Breathing Exercises: Practice deep breathing techniques or prenatal yoga to improve lung capacity and relaxation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep the respiratory mucous membranes moist and aid easier breathing.
- Avoid Triggers: Steer clear of smoke, strong odors, or allergens that might exacerbate breathing difficulties.
- Rest and Relaxation: Take regular breaks and prioritize rest to ease the strain on the respiratory system.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy isn’t just about the growing baby; it’s also about supporting your own respiratory health. Making mindful choices can significantly impact your breathing and overall well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in prenatal exercises approved by your healthcare provider to enhance lung function and overall stamina.
- Healthy Diet: Consume balanced meals rich in nutrients and avoid overeating, which can put pressure on the diaphragm.
- Monitor Weight Gain: Maintain a healthy weight throughout pregnancy to reduce additional stress on breathing.
- Sleeping Position: Lie on your side with pillows for support to alleviate pressure on the diaphragm.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation or prenatal massage to reduce stress, which can impact breathing.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothes to avoid restricting the chest area and allow comfortable breathing.
These adjustments can significantly alleviate breathing shortness during pregnancy, but it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and care.
Medical Interventions and Treatments
While the issue of difficult to breath during pregnancy is manageable with lifestyle adjustments and self-care techniques, some situations may necessitate medical intervention. Consulting with healthcare providers becomes crucial in ensuring the safety and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Here are some medical interventions and treatments that might be considered:
Oxygen Therapy
In cases where breathing difficulties are severe or persistent, supplemental oxygen therapy may be prescribed. This involves the use of oxygen delivered through a mask or nasal prongs to enhance oxygen levels in the blood, alleviating symptoms of breathlessness and ensuring adequate oxygen supply to both the mother and the fetus.
Medications
Healthcare providers may recommend specific medications to address underlying conditions contributing to breath shortness during pregnancy. For instance, if asthma exacerbations occur or if allergies are impacting respiratory function, appropriate medications may be prescribed to manage these conditions safely during pregnancy.
Physiotherapy
Engaging in specialized physiotherapy sessions tailored for pregnant individuals experiencing breathing difficulties can be beneficial. These sessions focus on breathing exercises, postural correction, and gentle movements aimed at improving lung capacity and easing breathing discomfort.
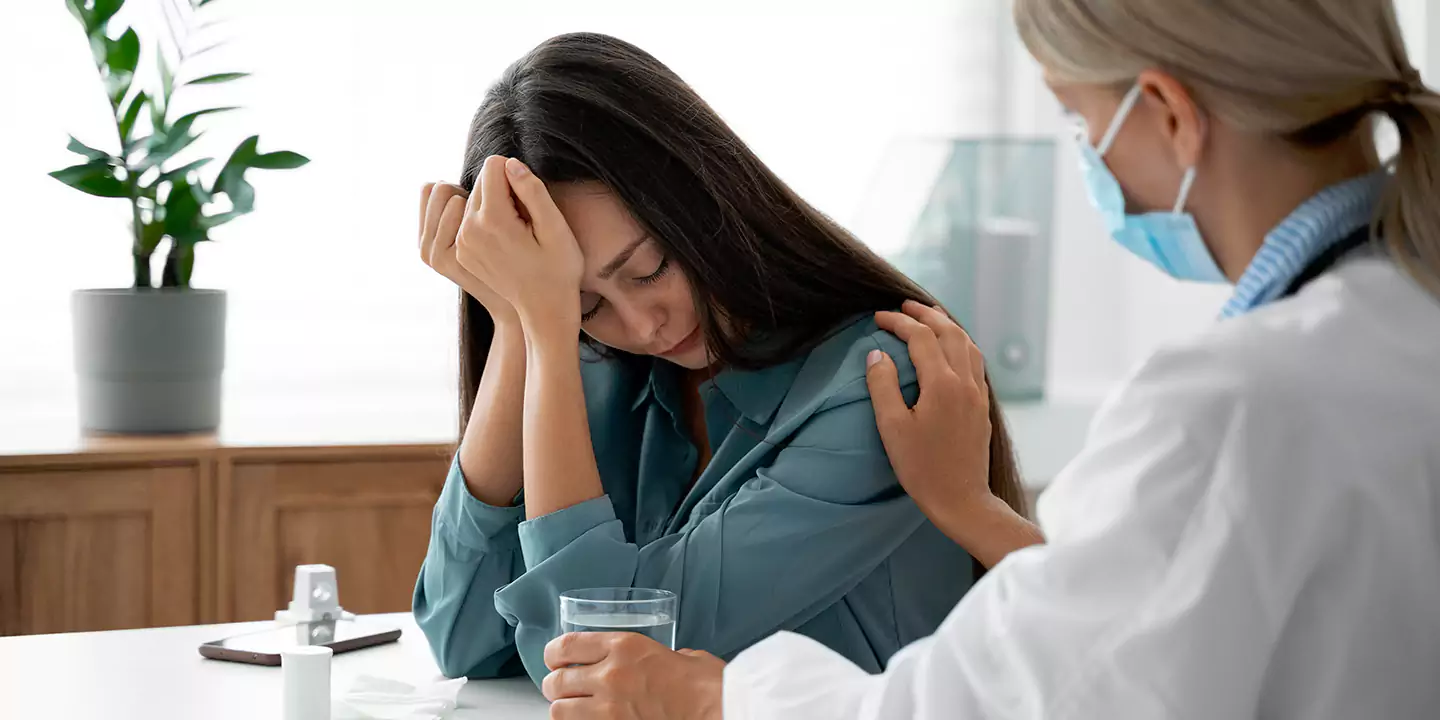
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
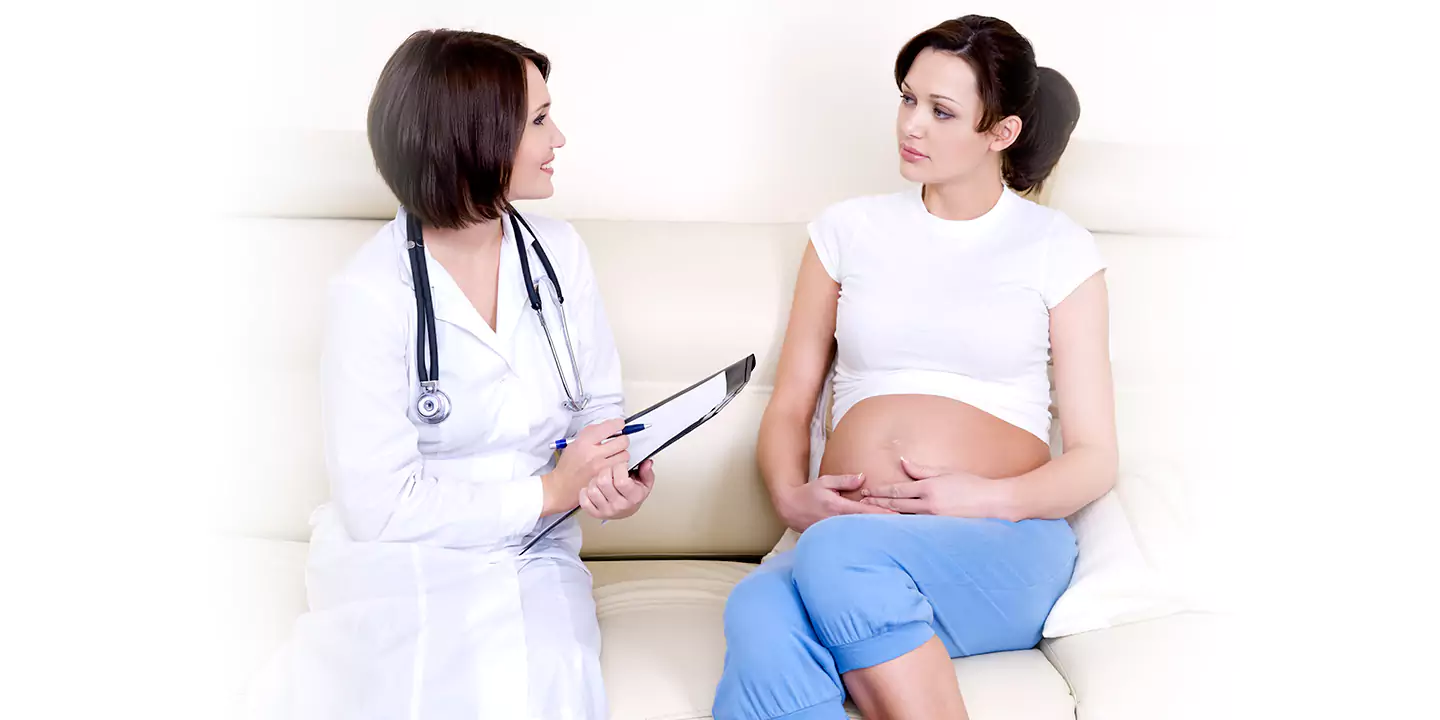
Continuous monitoring through regular prenatal check-ups is vital. Healthcare providers will assess the progression of breathing difficulties, monitor the baby’s growth and development, and address any emerging concerns promptly.
Obstetric Care and Delivery Planning
For individuals with severe respiratory issues, collaborative care between obstetricians and respiratory specialists may be necessary. Planning for labor and delivery involves ensuring optimal conditions to manage breathing challenges during the birthing process.
It’s crucial to approach any medical interventions or treatments under the guidance and supervision of qualified healthcare professionals. Open communication with your healthcare provider regarding any concerns or changes in symptoms is paramount to receiving appropriate care and support throughout your pregnancy journey.
Why Choose Queen’s Gynaecology?
At Queen’s Gynaecology, we understand the significance of a woman’s health journey, especially during pivotal phases like pregnancy. With a dedicated team led by Dr. Priya Shukla and Dr. Ruchi Tandon, our center specializes in comprehensive care, offering solutions that align with the unique needs of women experiencing the breathing problem during pregnancy.
Queen’s Gynaecology serves as a strong support, offering not just world-class laparoscopic and cosmetic surgeries but also a wealth of knowledge through our platform, Queen’s Health.
Join us in navigating the complexities of women’s health, gaining insights, and finding solace in a community that values your well-being. From understanding symptoms to staying informed, this space provides clarity on often overlooked complications. For personalized assistance on the breathing problem during pregnancy, connect with Queen’s Gynaecology for expert guidance. Your health, your priority.