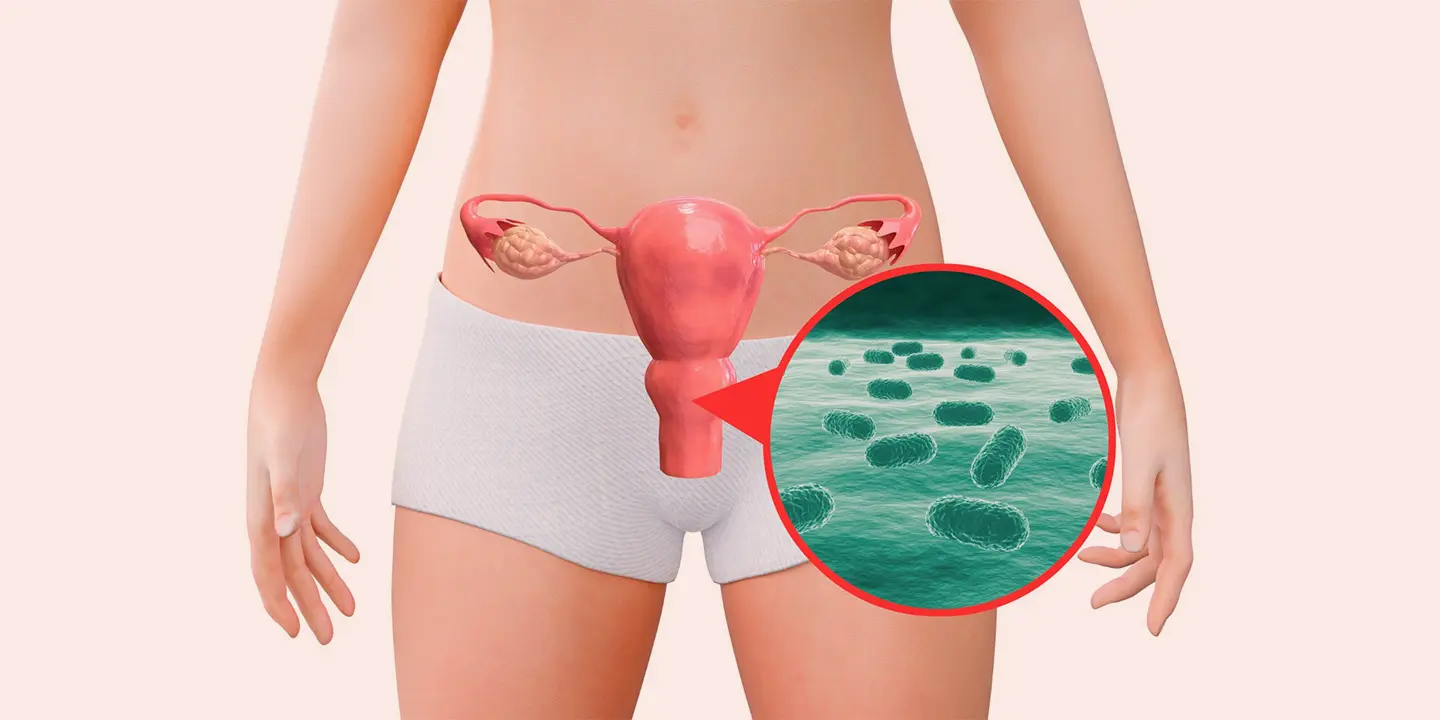
STIs should be taken seriously as many are there who overlook these infections that can be life-threatening. Over 30 viruses, bacteria, and parasites are known to be transmitted through physical sexual contact, including vaginal, anal as well as oral sex. There are a few STIs that can also be transmitted from mother to unborn during pregnancy, delivery, and breastfeeding. STIs have a severe impact on sexual as well as reproductive health worldwide, and thus, there is a need to consult the best gynecologist to get yourself tested for early diagnosis and STI treatment. Queen’s Gynecology is among the best clinics in Delhi, offering treatments for all types of women-related issues.
In this Article
- 1 What are sexually transmitted infections?
- 2 Unprotected sex and STI symptoms
- 3 Types of STIs
- 4 What to do if you think you have an STI?
- 5 How do you find out the proper STI testing?
- 6 Types of STI testing
- 7 What to do when a person is diagnosed with an STI infection?
- 8 How does Queen’s Gynecology help you to treat STIs?
What are sexually transmitted infections?
Sexually transmitted infections, also known as STIs, are infections that are passed from one person to another via sexual contact and can affect anyone sexually active, whether a person is single, married, or actively dating. These severe infections often don’t show any symptoms, and in medical terms, infections are considered diseases if they show signs; this is now more commonly termed a sexually transmitted disease(STD). Mainly STIs are transmitted by sexual contact as infections are passed from person to person through semen, blood, or vaginal fluids. However, there are cases in which infections can be transmitted non-sexually as well, either via blood transfusions or sharing the same needles or during pregnancy from mother to fetus.
STIs do not always cause symptoms and are contracted by people who seem healthy and who may not even be aware they have an infection because they don’t show any STI symptoms, and this is the reason experts say that STIs lead to STDs. Teens, young adults, and men who have sex with men are more prone to STI infections. And people who have an STI may be at higher risk of contracting HIV as well.
Unprotected sex and STI symptoms
Unprotected sex can happen, even if you take precautions and are at best intentions. Sometimes, it’s challenging to know what to do after unprotected sex, and the best way is to keep a check on STI symptoms to get treated immediately.
If you experience symptoms after unprotected sex like :
STI symptoms for women
- Unexplained or sudden bleeding
- Pain during or after intercourse
- Pain while peeing
- Pain in the lower tummy
- Unusual discharge
- Itching around the genital area or anus
- Sores or else rashes around the genital area or anus
STI symptoms for men
- Bleeding
- Penis Discharge
- Pain during ejaculation
- Testicles tenderness
- Rectal passage discharge
- Rashes or sores around the genitals
If you are experiencing any one or more than one type of STI symptoms, you should get yourself checked and talk to your gynecologist.
Types of STIs
There are many types of STIs, all with different effects:
- Chlamydia
It is a very common STI that often has no symptoms, making it particularly difficult to notice. Some symptoms may include pain while peeing, bleeding between periods, pain in the abdomen, and discharge from the penis or vagina.
- Gonorrhea
It spreads through vaginal, anal, as well as oral sex. People won’t experience any symptoms. However, people may experience thick green or yellow vaginal discharge or penis discharge, bleeding between periods and pain while peeing.
- Genital herpes
It is a common STI that spreads by having vaginal, anal, or else oral sex with someone who already has a STI infection. Many don’t realize that they come into contact with this STI; some symptoms include sores appearing as one or more blisters on or around the genitals.
- Hepatitis B
It is the most common STI that spreads in many ways. It spreads through bodily fluids during intercourse, from mother to newborn during birth, or via unsafe injections. People might experience stomach pain, nausea, fatigue, and jaundice.
- HIV
The most common STI attacks cells that help the body fight infection. Untreated HIV leads to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, i.e., AIDS. People may experience flu-like symptoms within two to four weeks of becoming infected.
- HPV infection
It is an extremely common STI that is spread mainly by vaginal sex but rarely from skin-to-skin touching. In terms of symptoms, people do go on to develop genital warts.
- Syphilis
Syphilis is a common curable STI with four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. In the first stage, people experience single sores or multiple sores. During the second stage, people develop rashes or sores. In the third stage, there will be no visible signs and symptoms. Infected people generally do not develop the final (tertiary) stage.
- Trichomoniasis
It is a common STI that spreads by having sex without barrier protection. Generally, people experience itching, irritation, or burning sensations in the genital area and foul-smelling discharge.
What to do if you think you have an STI?
Not all STI symptoms are noticed, which is why it’s vital to get tested regularly, especially every time you have unprotected sex. The best women’s health clinics offer many STI testing schemes. If you test positive for an STI, your gynecologist should be able to help you with proper treatment, as each one will need different treatments.
- STI screening
STIs mostly have no symptoms, and testing is the only way to know if you have an infection. So if you’ve had any kind of sexual contact that can spread STDs — like vaginal, anal, or oral sex — talk to your gynecologist about getting STI treatment.
- STI treatment
The idea of getting an STI screening or a test for sexually transmitted infection may seem problematic, but no need to be stressed. Most common STIs can be easily cured with medications. There are many treatments to help you with symptoms and to lower your chances of STI spreading. Thus, the earlier you know you have an STI, the faster you can start caring for yourself and your partner. It’s extra vital to get tested if you’ve had unprotected sexual contact or if you find out that your partner already has an infection.
How do you find out the proper STI testing?
Women are unaware of the STI testing they need. By asking your gynecologist, you can get expert advice. They will help you to know the best screenings for you.
Many factors may affect your STI screening needs, including:
- Relationship status
- Multiple partners
- your history of unprotected sex
- History of STIs
- If you are trying to become pregnant
- If you are currently pregnant
Types of STI testing
Testing for STIs may be more accessible and can be completed in one visit. Testing involves quick tests like taking blood samples, a swab, or urine tests.
Some of the most common STI tests are :
- For Gonorrhea and chlamydia: urine test and genital swab
- For Herpes: a blood test and a swab if you have symptoms
- For Trichomoniasis, a swab or sample of fluid
- For Syphilis: blood test if you have symptoms
- For HIV: blood test or a mouth swab
What to do when a person is diagnosed with an STI infection?
First, it is vital to understand that STIs need immediate and proper treatment. It is impossible that the infection will go away on their own. Additionally, if STI remains untreated, you are more prone to further health complications, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, tubal or else ectopic pregnancy, perinatal or congenital infections in newborns, etc. You also risk spreading the infection to others as well.
Thus, the time you get diagnosed with STIs :
- Get treated
- Tell your partner or partners clearly
- Understand well that STIs can be managed and treated well.
- To prevent getting an STD or Sexually transmitted infection, always avoid sexual contact with someone who has genital sores, a rash, discharge, or any other symptoms.
- Always use condoms while having intercourse
- Always get on time for STI testing to prevent it.
How does Queen’s Gynecology help you to treat STIs?
Irrespective of the cause, the sooner you get treated, the less likely you will face long-term complications and it also reduces the chances that you are to spread your condition to others. Expert gynecologists at Queen’s Gynecology help you diagnose and treat STIs by putting you on antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Proper diagnosis is vital before starting the appropriate treatment. It is best for the STI screening tests or urine tests suggested by a gynecologist.
If a person has open sores on the genital portion, the doctor will collect fluid samples to help diagnose the infections. If STIs occur because of bacteria, then these are treatable with the help of medications. But, if it comes from viruses, then complete cure. Initial treatments will provide you with excellent results. STIs can be severe if people keep them untreatable, and they can be life-threatening in some manner if undetected. The gynecologist at Queen’s Gynecology will treat the matter with sensitivity and confidentiality. The main goal of the gynecologist is to diagnose the condition and advise an STI treatment plan to help the patient feel well.