With more than 6 million new cases a year, Tuberculosis (TB) has become an alarming health concern around the globe. It is a form of bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis that initially affects the lungs. TB can have a devastating impact on the people and usually occurs in two forms, pulmonary tuberculosis and extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
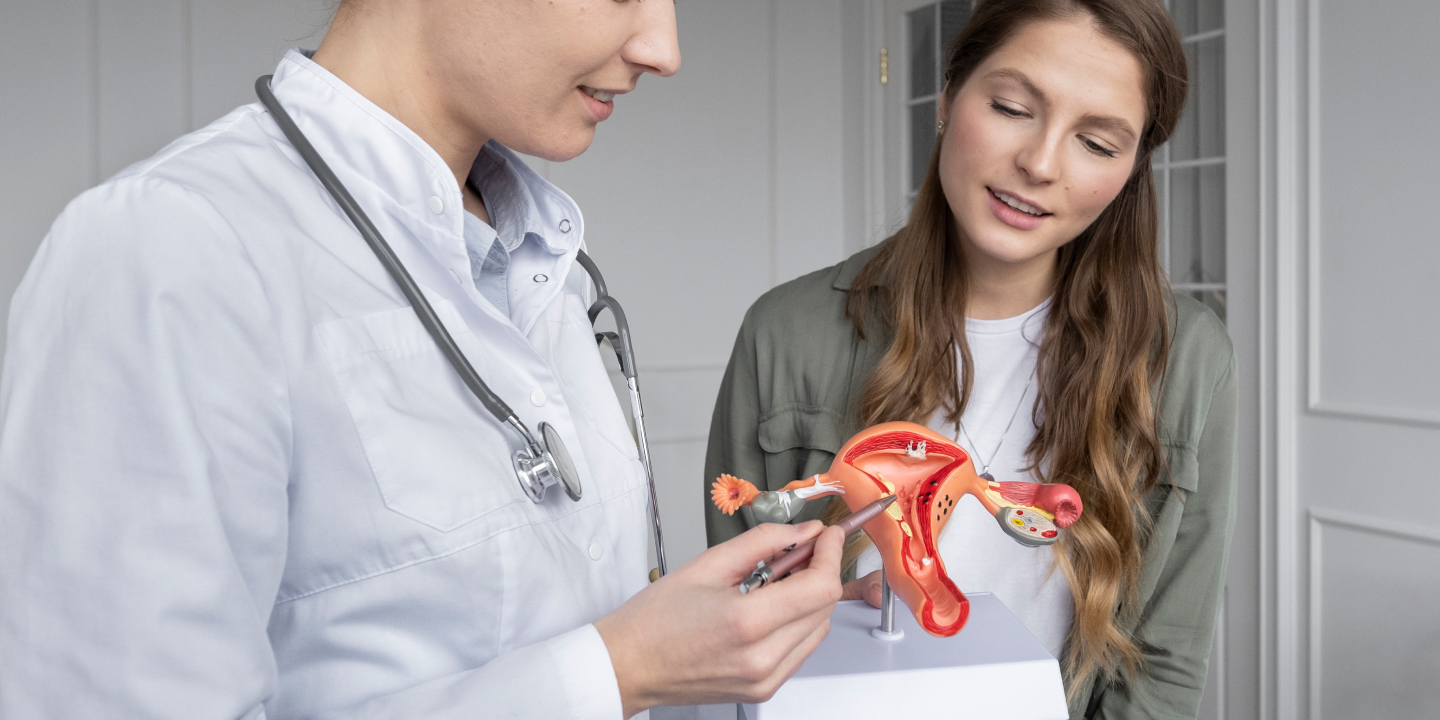
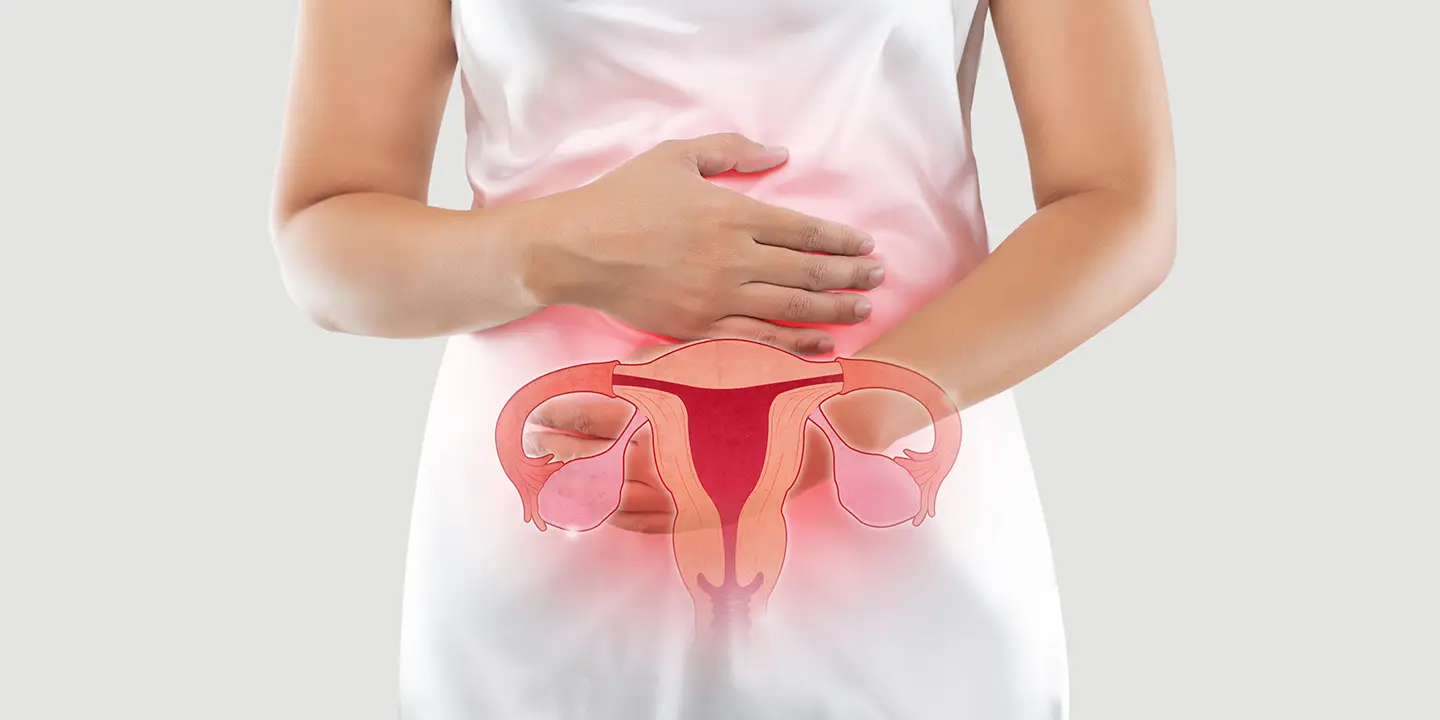
Genital tuberculosis belongs mainly to the category of extrapulmonary tuberculosis that affects the female genital organs. It can also affect the surrounding lymph nodes in the pelvis. It can occur to women of any age, but women of reproductive age (15-45 years) are more vulnerable to the condition.
Related Blog – Important Things Female and Teen Should Know About Ovarian Cysts
In this Article
Causes of Genital Tuberculosis
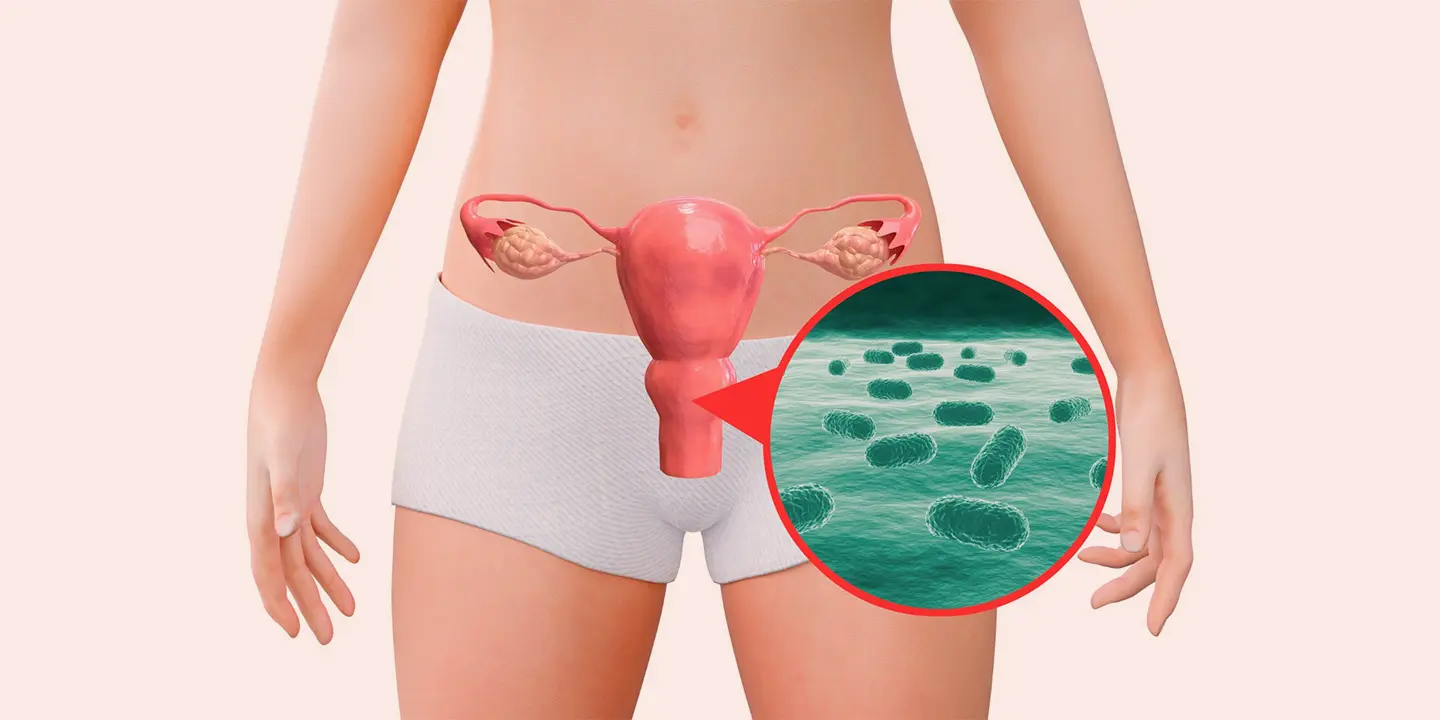
According to some research, Mycobacterium tuberculosis are responsible for 90-95% cases of genital TB. They are contagious in nature and can spread from one person to another just by the inhalation of droplets produced during talking, coughing and sneezing. They can attack the genital tract through four routes: descending direct spread, lymphatic spread, haematogenous route (primary focus is lungs), and primary infection of the genitals through sexual intercourse.
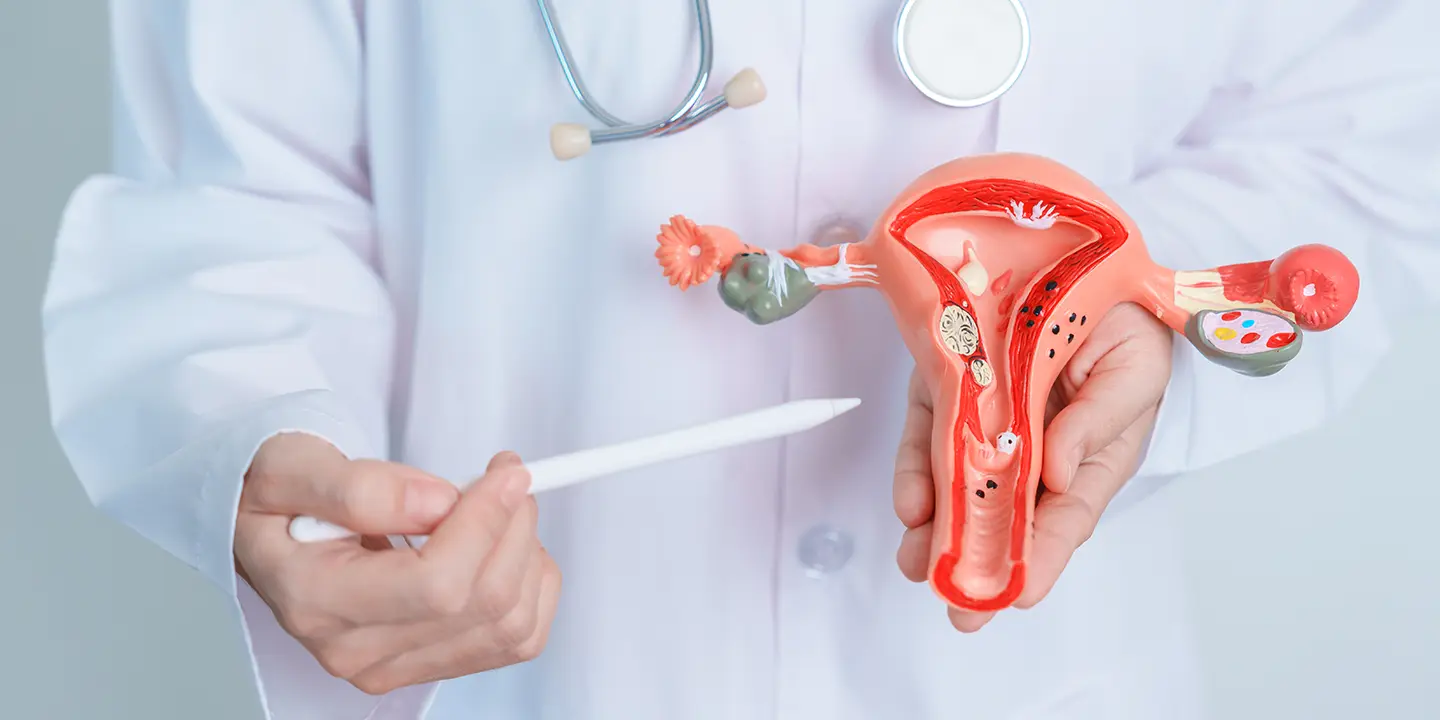
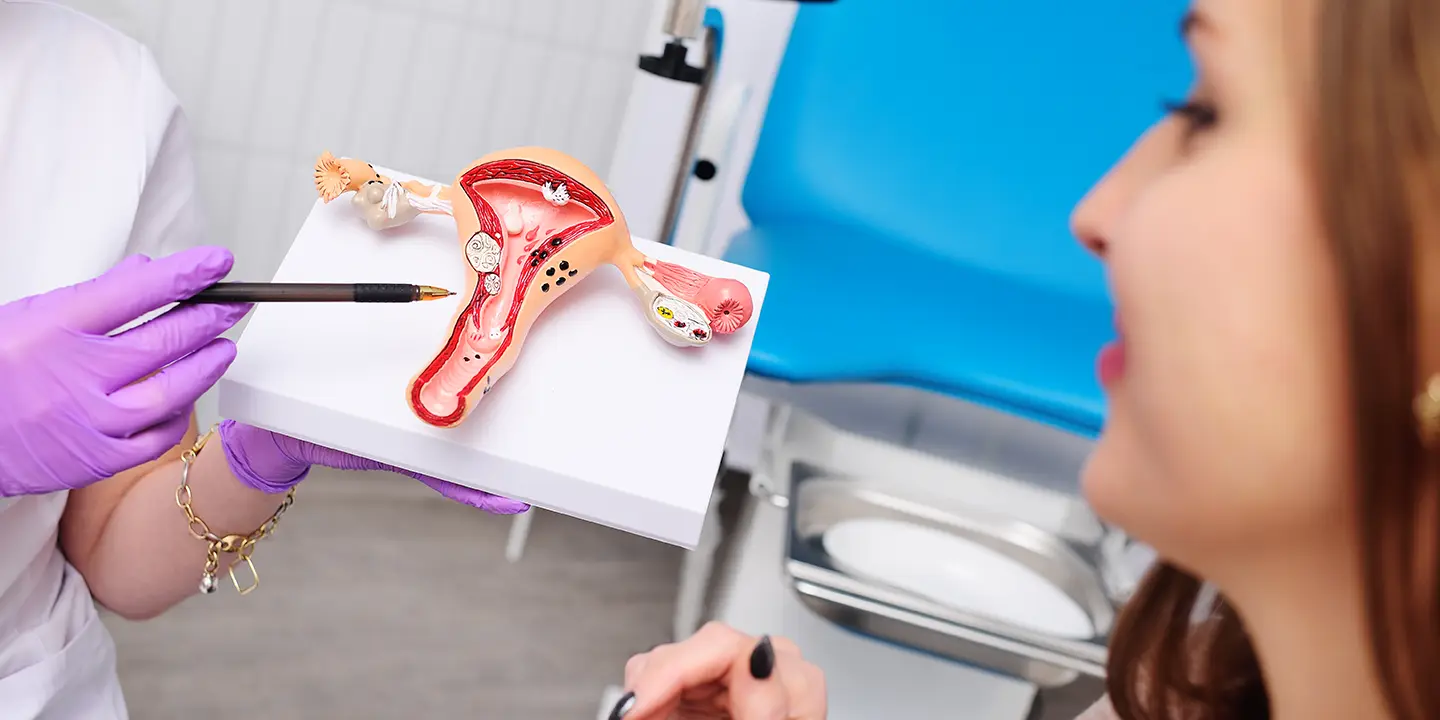
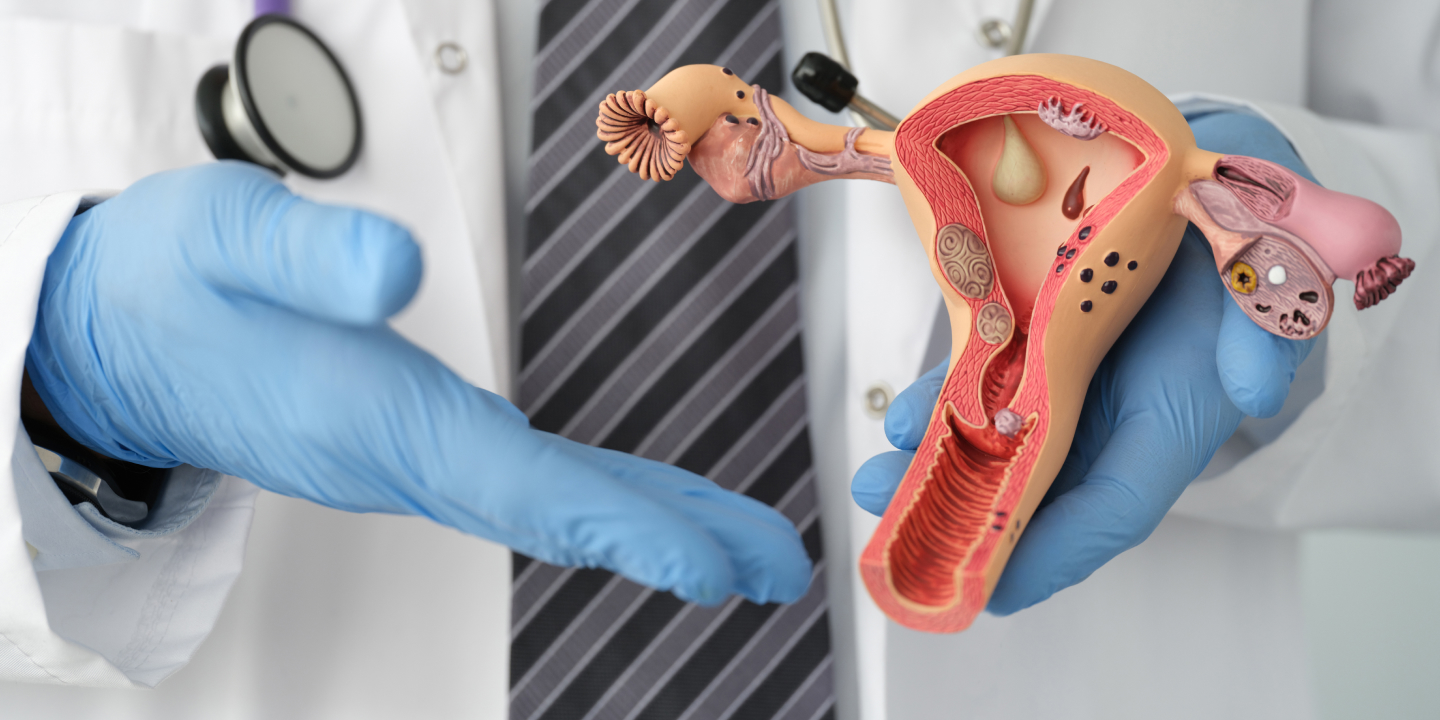
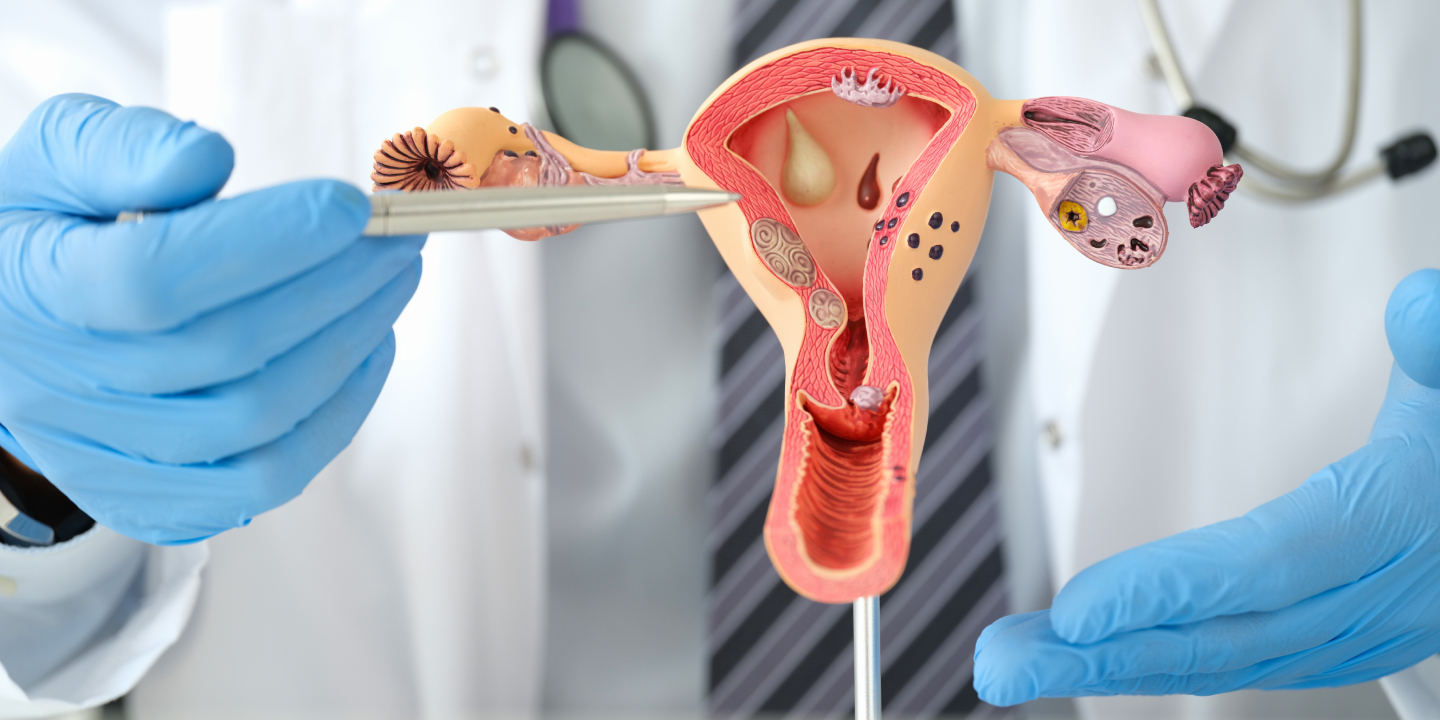
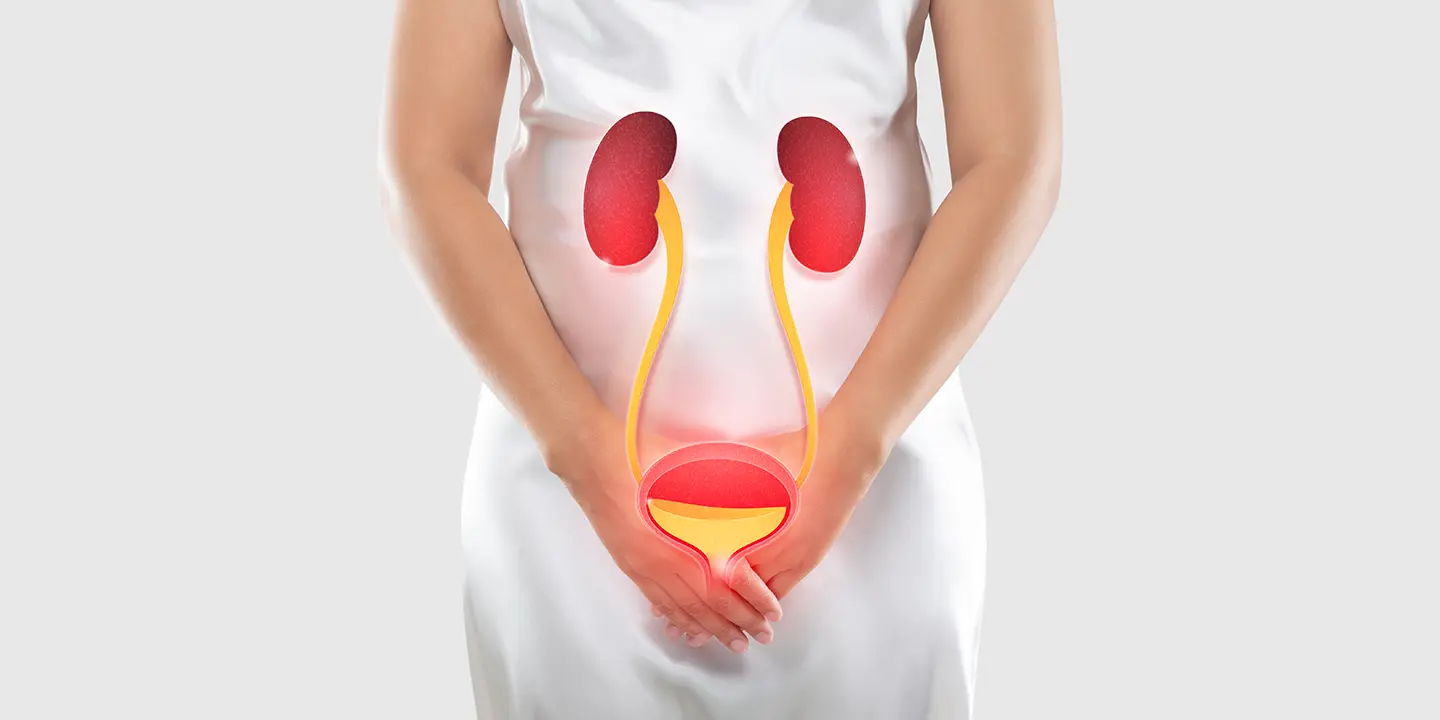
The genital organs affected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis include the fallopian tube, uterine endometrium, ovaries, cervix, uterine myometrium, and vagina/vulva.
Symptoms of Genital Tuberculosis
According to the best gynecologists in Delhi, genital tuberculosis can be asymptomatic in nature. Besides, it may be disguised for other gynecological conditions, especially infertility. Some of the other possible signs and symptoms include:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Irregular periods
Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital Tuberculosis
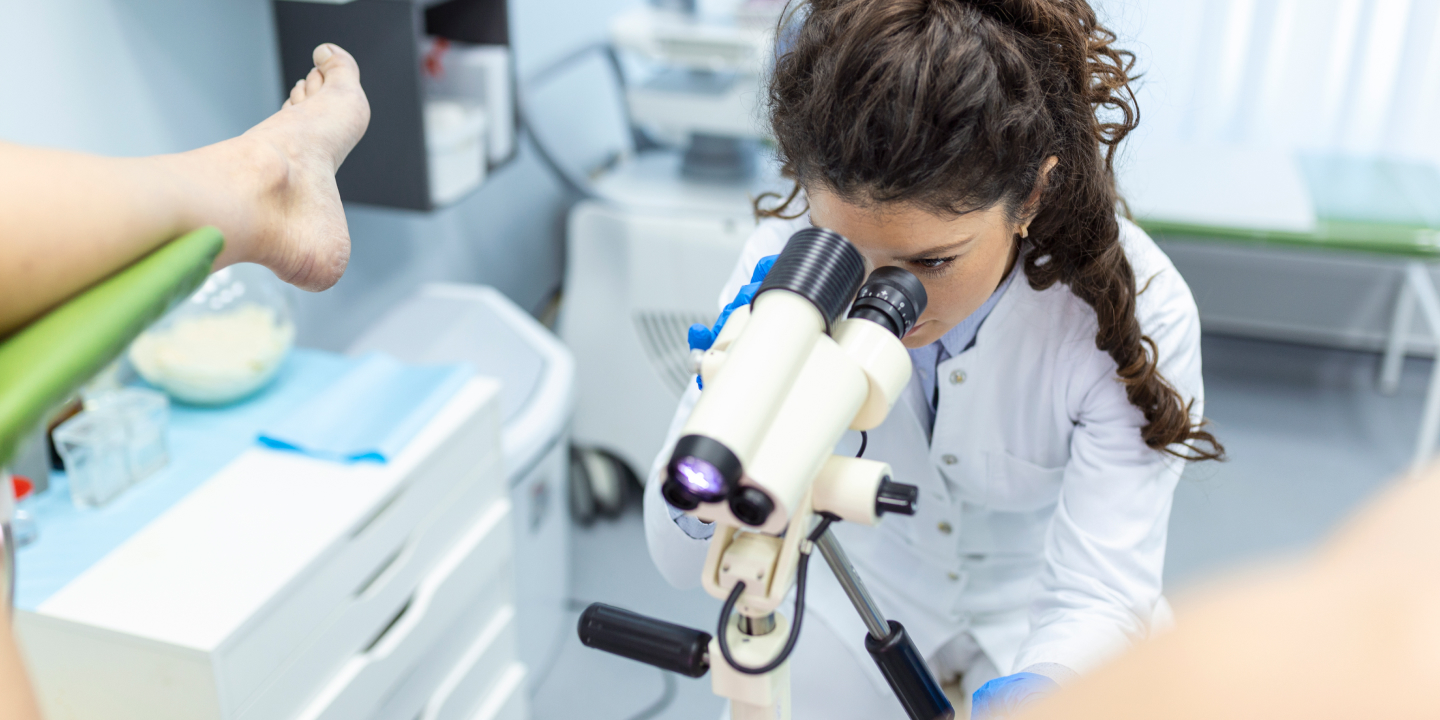
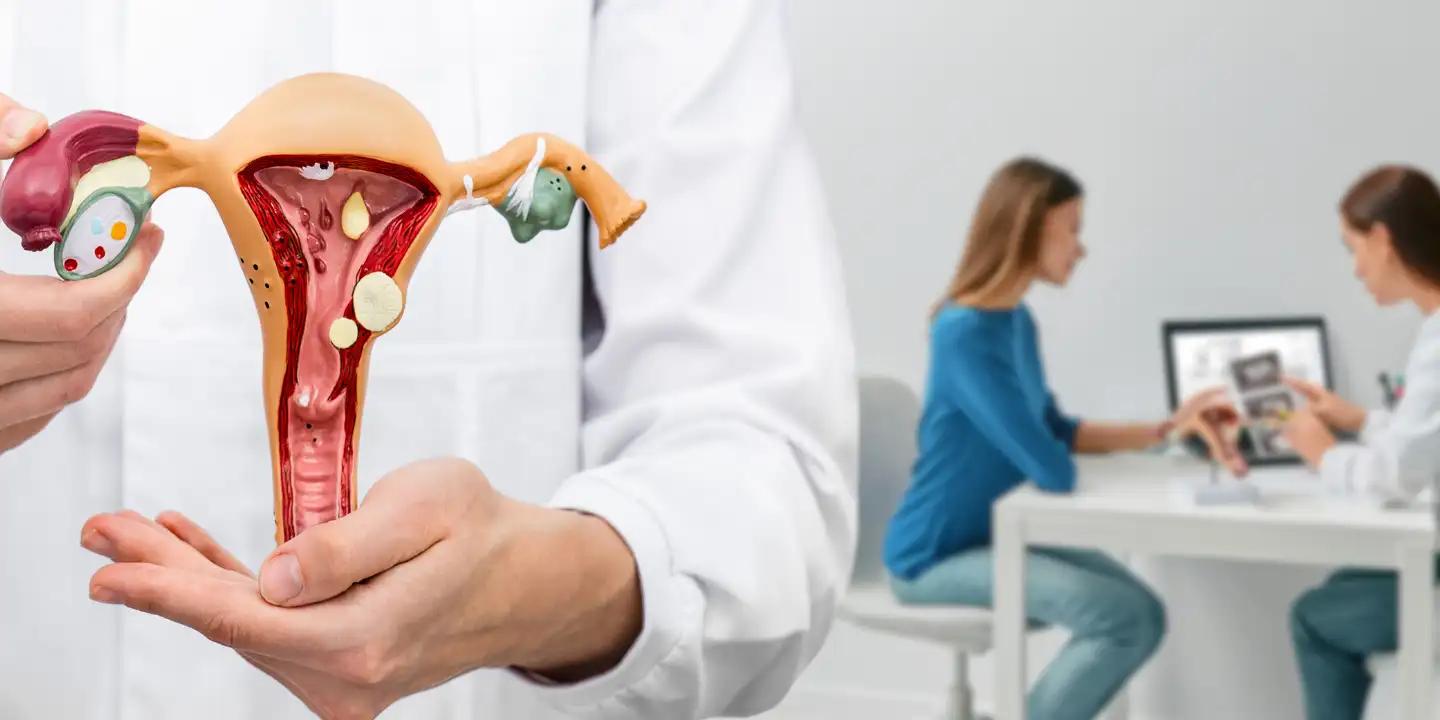
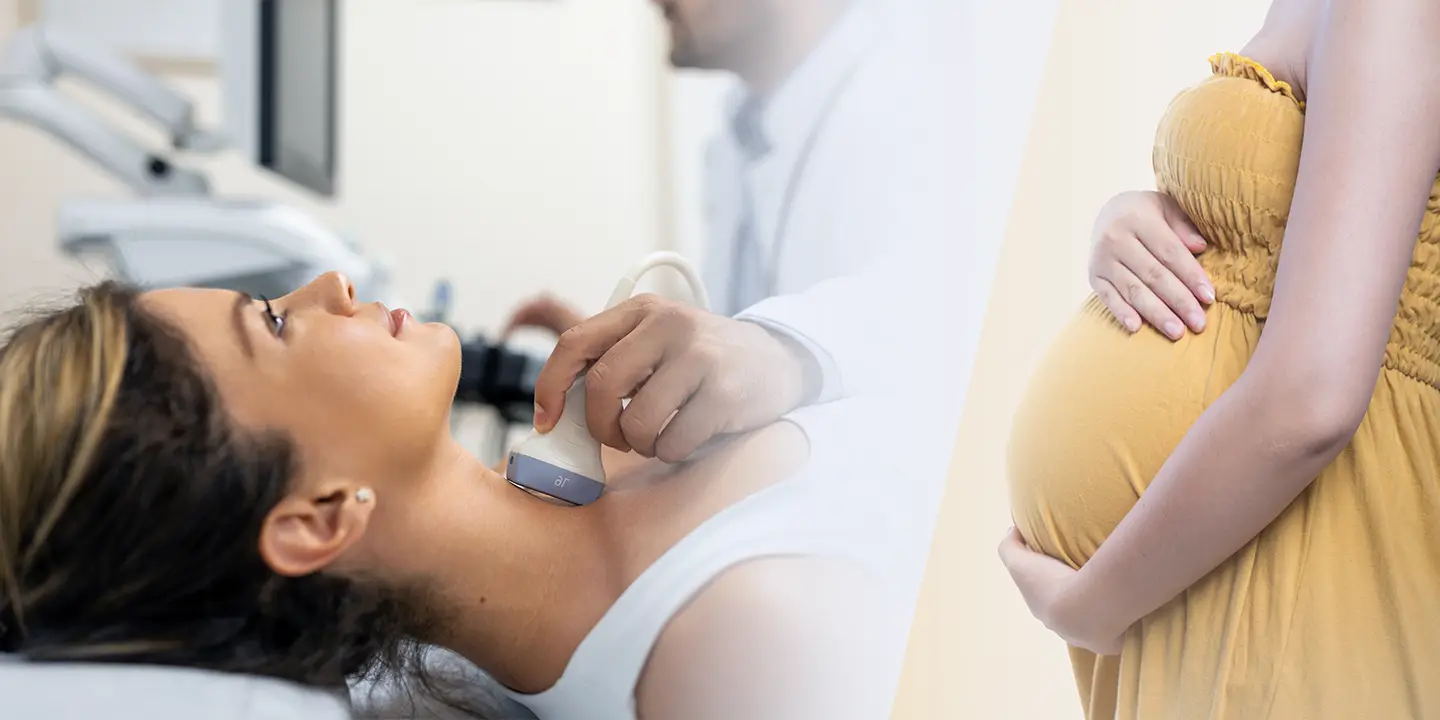
As genital tuberculosis is mainly asymptomatic, it needs a systematic clinical examination, high degree of suspicion, extensive history taking, battery of tests, and imaging methodologies for proper diagnosis. For early diagnosis, you must visit the best gynecology clinics wherein top gynecologists perform various tests such as chest X-ray, pelvic ultrasound scan, cervical smear examination, endometrial curettage, menstrual blood analysis, and laparoscopic examination for the detailed analysis of genital tuberculosis.
After proper diagnosis, your gynecologist may offer a variety of treatments which include multidrug regime as per the Directly Observed Treatment Short course (DOTS). This treatment is divided into two phases: the initial therapy that consists of 3 anti-TB drugs for 2 months along with a continuation phase that includes 2 anti-TB drugs for another 4-10 months.
Furthermore, a surgical treatment of the affected areas might be required in the complex cases of genital TB or in the cases of drug resistance. In addition to this, IVF is performed in cases of infertility.
Early diagnosis along with effective treatment is the road to a healthy living. So if you are experiencing any of the above-mentioned signs and symptoms, you should immediately visit the top gynecology clinic wherein specialised gynecologists are known to offer the best treatment for genital tuberculosis in Delhi.
Related Blog – Ovarian Cyst and its Impact on Pregnancy and Fertility