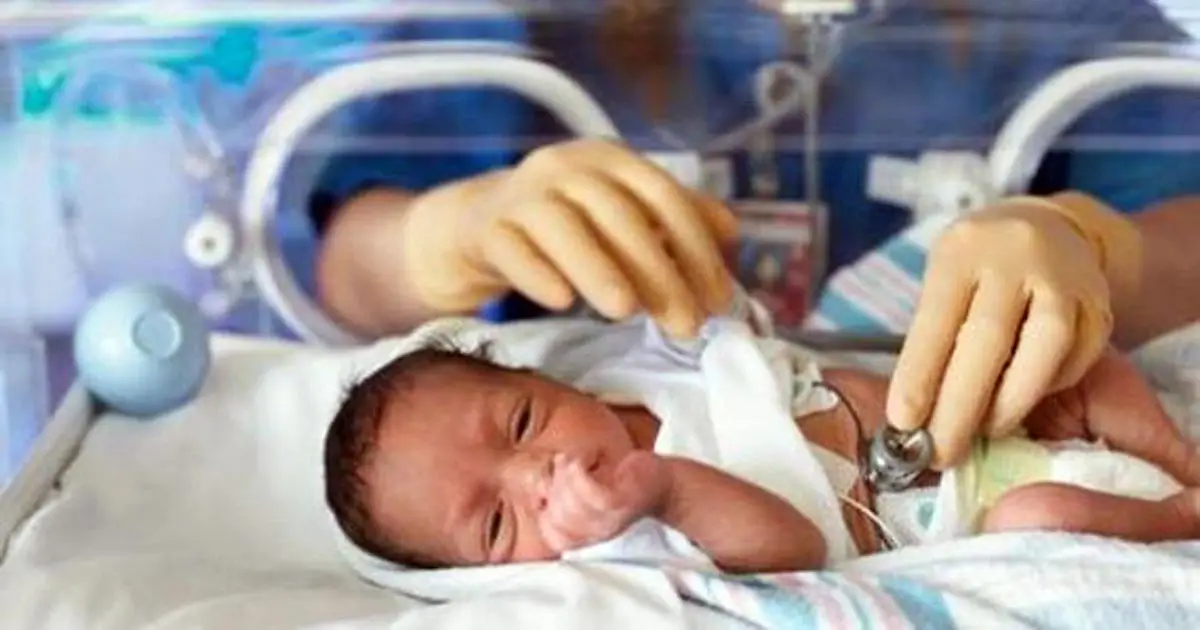
More than 1 in 10 babies are born preterm every year and the number will continue to increase. India witnesses the highest number of preterm births, followed by China and Nigeria. However, the highest rate of preterm births per 100 live births is in Malawi. Before discussing the risks associated and the factors leading to preterm births, let us understand the basics of preterm.
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes preterm birth as the delivery in which a baby is born alive before the completion of 37 weeks of gestation.
There are different stages or categories of preterm birth:
- Extremely Preterm: babies born before 28 weeks of gestation
- Very Preterm: babies born between 28 to 32 weeks of gestation
- Moderate to Late Preterm: babies born between 32 to 37 weeks of gestation.
In this Article
Why Does Preterm Birth Occur?
Preterm births can happen due to a variety of reasons. Sometimes they are a spontaneous occurrence whereas other times there may be an underlying reason.
Some common causes include:
Multiple pregnancies: When IVF results in multiple pregnancies, the risk of preterm birth of each of the babies increases.
Diabetes: If the mother is diabetic, she may give birth preterm.
High Blood Pressure: It is another chronic condition that often leads to preterm births.
Smoking: If the mother used to smoke before or during pregnancy.
Drinking: Drinking alcohol during the gestation period.
Medication and drugs: Certain medications, all illegal drugs, and tobacco may cause preterm births.
Physical Trauma: Any kind of physical trauma resulting from a fall or any other accident often results in preterm birth.
Anatomical conditions: Shorter or weak cervix often leads to preterm births.
Abnormal amount of amniotic fluids: Women with more amniotic fluid than required (polyhydramnios) and less amniotic fluid than needed (oligohydramnios) are at high risk. Anxiety and Depression: These psychological conditions also cause preterm births in many. Infections: Bacterial, yeast, and other vaginal, urinary tract, uterus, and fetal infections have also been linked to preterm births.
History of Preterm Birth: Close pregnancies and earlier cases of preterm births increase the risk of another preterm.
Insufficient nutrition: Expecting mothers with low body mass index and poor nutritional status cause preterm births too.
Other causes like air pollution, fertility medicines, and more also enhance the risk of preterm births.
Symptoms of Preterm Birth:
- Frequent contractions: In every ten minutes or less, there will be a contraction.
- Increase in vaginal discharge: Blood and white discharge will increase.
- Immense pelvic pressure: The feeling that the baby is pushing downwards.
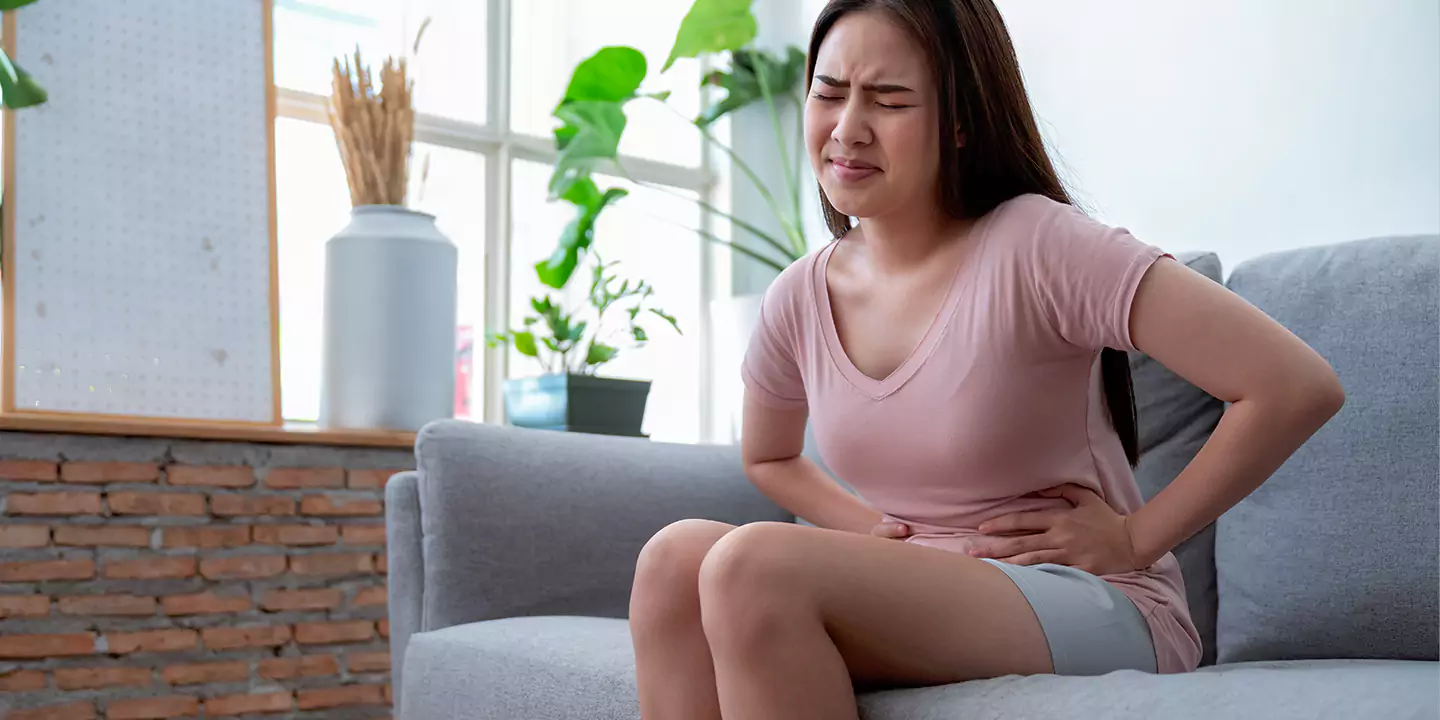
- Lower back cramps: Back pains become more common.
- Abdominal cramps: Lover abdominal cramps are also an indicator of Preterm Birth.
- Diarrhea: May or may not occur in all.
Risks for the baby:
1. Difficulty in eating
2. Breathing difficulties
3. Cerebral Palsy
4. Delay in physical and mental development
5. Problems in vision Auditory problems
Preventive Measures To Avoid
1. Access to a gynecologist before and during pregnancies.
2. Identifying the risks at an early stage for effective treatments.
3. Preventing close pregnancies
4. Single embryo transfer during IVF (In-vitro Fertilization)