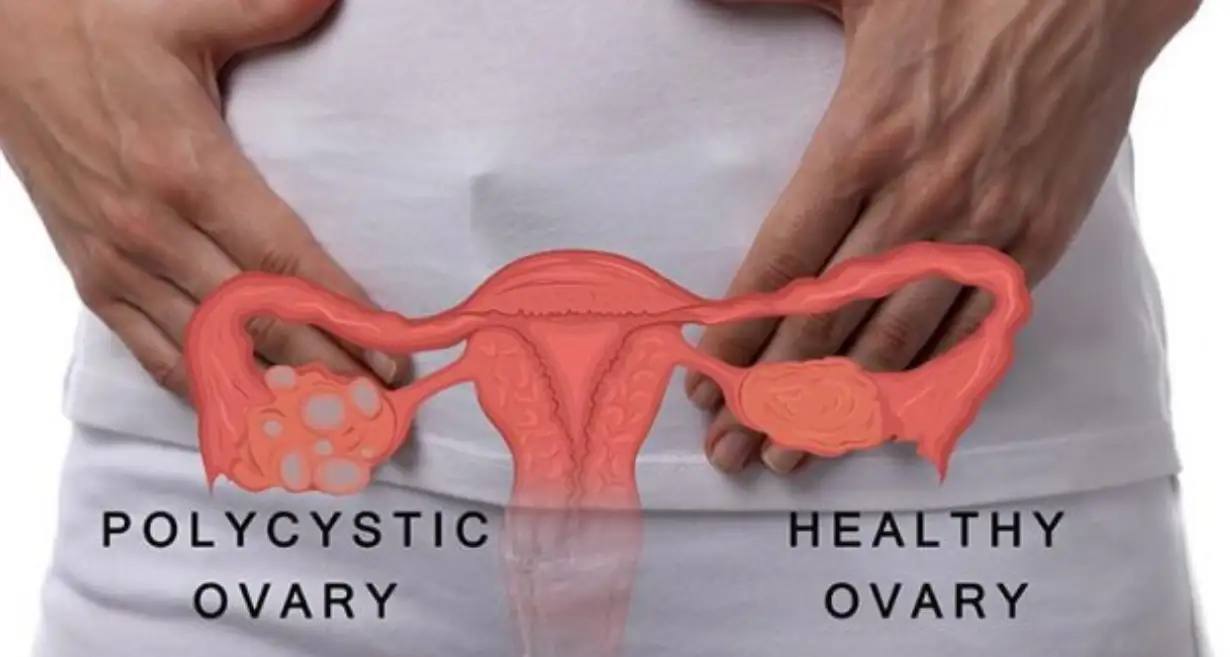
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women all around the world, and it can bring a variety of challenges, from irregular periods to fertility issues.
While there is no cure for PCOS, managing its symptoms through a balanced diet can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
In this guide, we’ll explore what to eat and what to avoid to help you navigate the world of PCOS-friendly nutrition.
By making mindful food choices, you can take steps toward better managing your PCOS and promoting your overall health and well-being.
In this Article
Overview
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects females of adolescent age, often causing hormonal imbalances that can further lead to issues with their health. It is characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts.
Here’s an overview of the foods you need to eat and avoid with PCOS:
| Foods to Eat | Foods to Avoid |
| Fruits and Vegetables: | Processed Sugars: |
| – Berries | – Sugary snacks and drinks |
| – Leafy greens | – High-fructose corn syrup |
| – Cruciferous vegetables | – Candy and desserts |
| Whole Grains: | Trans Fats: |
| – Quinoa | – Fast food and fried items |
| – Oats | – Packaged baked goods |
| – Brown rice | – Hydrogenated oils |
| Lean Proteins: | Dairy: |
| – Skinless poultry | – Full-fat dairy products |
| – Fish (salmon, mackerel) | – Sugary yogurts |
| – Legumes (lentils, beans) | High-Glycemic Carbs: |
| Healthy Fats: | – White bread |
| – Avocado | – Sugary cereals |
| – Nuts and seeds | – Instant oatmeal |
| – Olive oil | |
| Low-Fat Dairy: | Excessive Red Meat: |
| – Greek yogurt | – Processed and red meats |
| – Skim milk | |
| Herbs and Spices: | |
| – Cinnamon | |
| – Turmeric |
Types of Diet to Manage PCOS
Here are some types of diets that may be beneficial for individuals with PCOS:
1. Low Glycemic Index (GI) Diet:
· Focuses on consuming foods that have a low impact on blood sugar levels, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
· Helps regulate insulin levels and manage weight, a common concern for those with PCOS.
2. Mediterranean Diet:
· Emphasizes whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil and nuts.
· May improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote heart health.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Diet:
· Incorporates foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, berries, and leafy greens.
· Aims to reduce inflammation, a contributing factor to PCOS symptoms.
4. Low-Carb Diet:
· Limits the intake of carbohydrates, particularly refined sugars and starchy foods.
· Can help control insulin levels and manage weight.
5. High-Fiber Diet:
· Emphasizes fiber-rich foods like whole grains, legumes, and fruits and vegetables.
· Promotes digestive health, regulates blood sugar, and aids in weight management.
6. Gluten-Free Diet:
· Eliminates gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye.
· May be beneficial for individuals with PCOS who have gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
7. Balanced and Calorie-Controlled Diet:
· Focuses on portion control and ensuring a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats).
· Helps manage weight and insulin levels.
8. Vegetarian or Plant-Based Diet:
· Centers around plant-based foods, reducing or eliminating animal products.
· Can be rich in fiber and low in saturated fats, promoting hormonal balance.
Foods to Eat
Here are foods to include in your diet if you have PCOS:
- Fruits and Vegetables
Consume a variety of colorful fruits and non-starchy vegetables. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains
Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat products. They offer fiber and slow-release energy.
- Lean Proteins
Include lean protein sources like poultry, fish (salmon, mackerel), legumes (lentils, beans), and tofu.
- Healthy Fats
Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are beneficial for hormone regulation.
- Low-Fat Dairy
If you consume dairy, choose low-fat or fat-free options like Greek yogurt and skim milk.
- Herbs and Spices
Add herbs like cinnamon and turmeric, known for their potential to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Include foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish, berries, and leafy greens, to reduce inflammation.
- High-Fiber Foods
Prioritize high-fiber foods, including whole grains, legumes, and fibrous vegetables, which help regulate blood sugar and promote digestive health.
- Water
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Proper hydration supports overall health and can aid in weight management.
- Green Tea
Green tea may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that could benefit individuals with PCOS.
Foods to Avoid
Here’s a list of foods to be cautious of or avoid:
- Highly Processed Sugars
Foods and beverages with added sugars, like sugary snacks, sodas, and sweetened cereals, can lead to blood sugar spikes and worsen insulin resistance.
- High Glycemic Carbohydrates
Refined grains such as white bread, white rice, and instant oatmeal can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels. Opt for whole grains instead.
- Trans Fats
Trans fats, often found in fried and fast food, packaged baked goods, and products containing hydrogenated oils, can contribute to inflammation and insulin resistance.
- Full-Fat Dairy
High-fat dairy products, such as whole milk, full-fat yogurt, and cheese, can lead to weight gain and hormonal imbalances. Choose low-fat or skim options if you consume dairy.
- Excessive Red Meat
Consuming large amounts of red and processed meats can be linked to increased inflammation and insulin resistance. Try to limit your intake.
- High-Sodium Foods
Foods with high sodium content, like processed meats, canned soups, and salty snacks, can contribute to bloating and water retention.
- Caffeine and Alcohol
While small amounts are generally acceptable, excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption can affect hormone balance and overall health.
- Dairy Alternatives with Added Sugars
Be cautious with non-dairy milk alternatives, as they often contain added sugars. Opt for unsweetened varieties.
- Soy Products
While some soy can be part of a healthy diet, too much soy may affect hormonal balance, so moderation is key.
- High-Carb, Low-Fiber Foods
Foods lacking in fiber, such as pastries and white pasta, can lead to rapid blood sugar spikes. Choose fiber-rich alternatives instead.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage PCOS
Here are some essential lifestyle changes to consider when dealing with PCOS:
- Regular Exercise
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine. Exercise helps with weight management, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces inflammation.
- Weight Management
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. A combination of a balanced diet and exercise is essential for weight control.
- Stress Reduction
High stress levels can worsen PCOS symptoms. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness to promote emotional well-being.
- Adequate Sleep
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Proper sleep can aid in hormone regulation and support overall health.
- Hydration
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Proper hydration supports bodily functions and can help manage weight.
- Regular Check-ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. Monitoring your condition and discussing any necessary medications or treatments is crucial.
- Tracking and Monitoring
Keep a diary to track your symptoms, dietary choices, and exercise routines. This can help identify patterns and make necessary adjustments.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience the following symptoms:
- Acne
- Excessive facial or body hair growth
- Hair thinning
- Unexplained weight gain
- Skin darkening, notably in skin folds and creases
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Skin tags in the neck and underarm areas
- Challenges in conceiving
Conclusion
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing PCOS and improving overall health. By choosing nutrient-rich foods and avoiding those that can exacerbate symptoms, you can take steps towards a healthier, more balanced life.
For personalized guidance and expert advice on PCOS management, don’t hesitate to consult the specialists at Queen’s Gynecology. We have the best team of doctors to help you manage PCOS and enjoy a better life. Your journey to better health starts with the right support. Contact us today for a healthier tomorrow.
FAQ’s
Eggs can be a healthy protein source for managing symptoms of PCOS.
Bananas in moderation are fine for dealing with PCOS.
Almonds and walnuts are excellent nuts for managing symptoms of PCOS.
High-sugar fruits like watermelon and pineapple are best consumed in moderation to maintain the symptoms of PCOS.