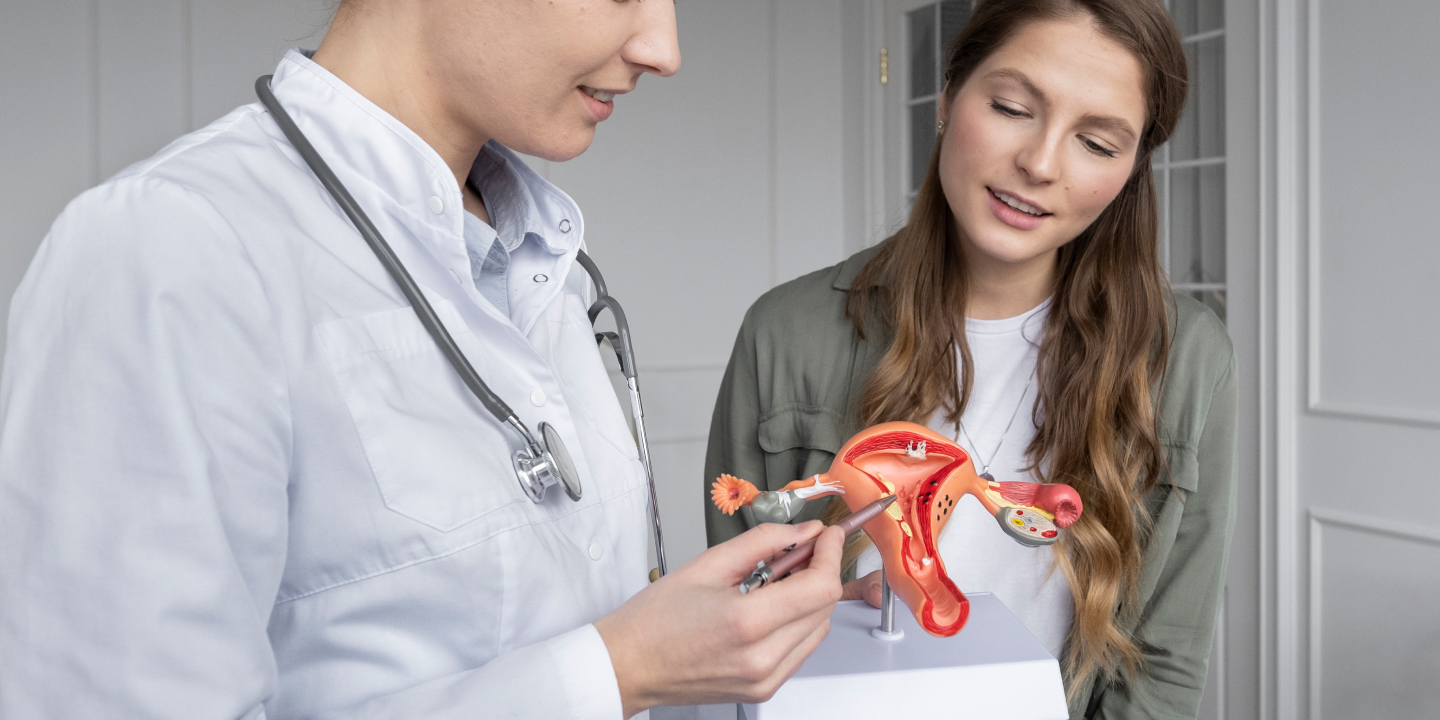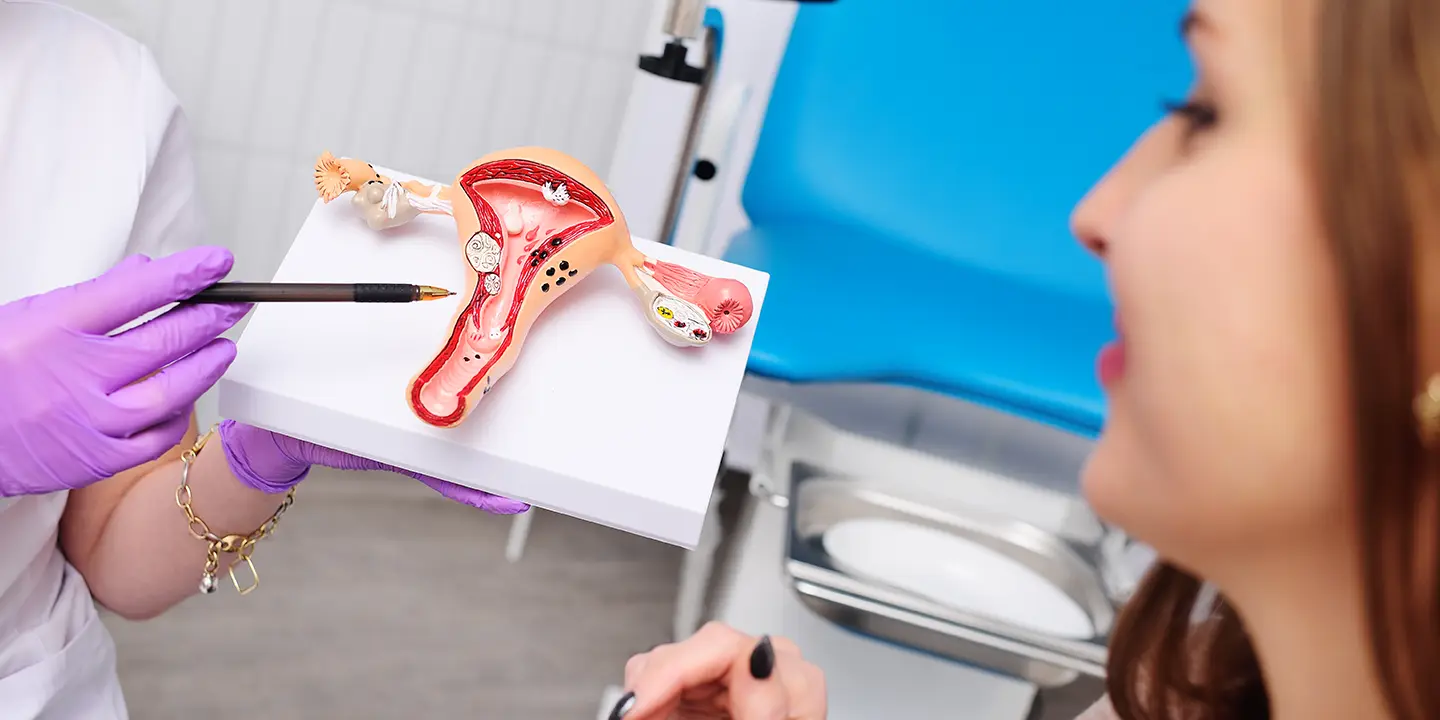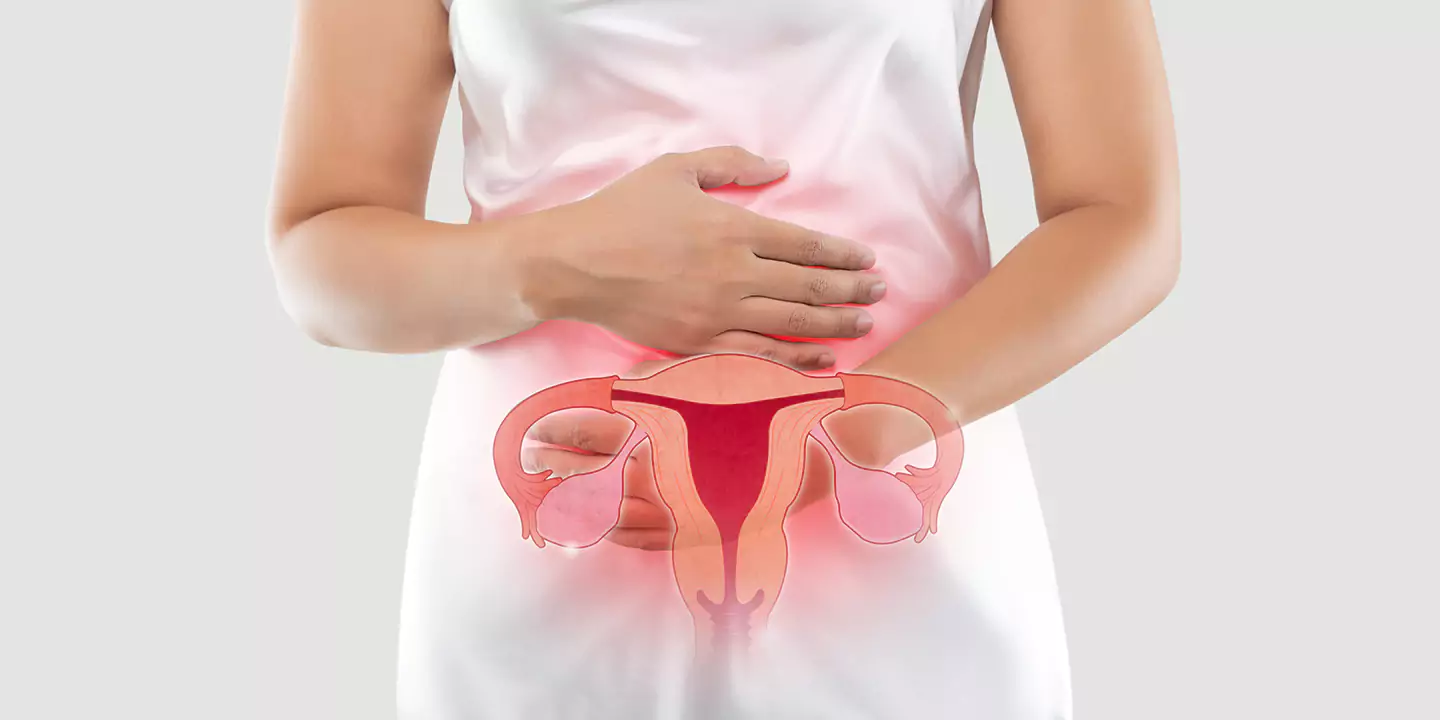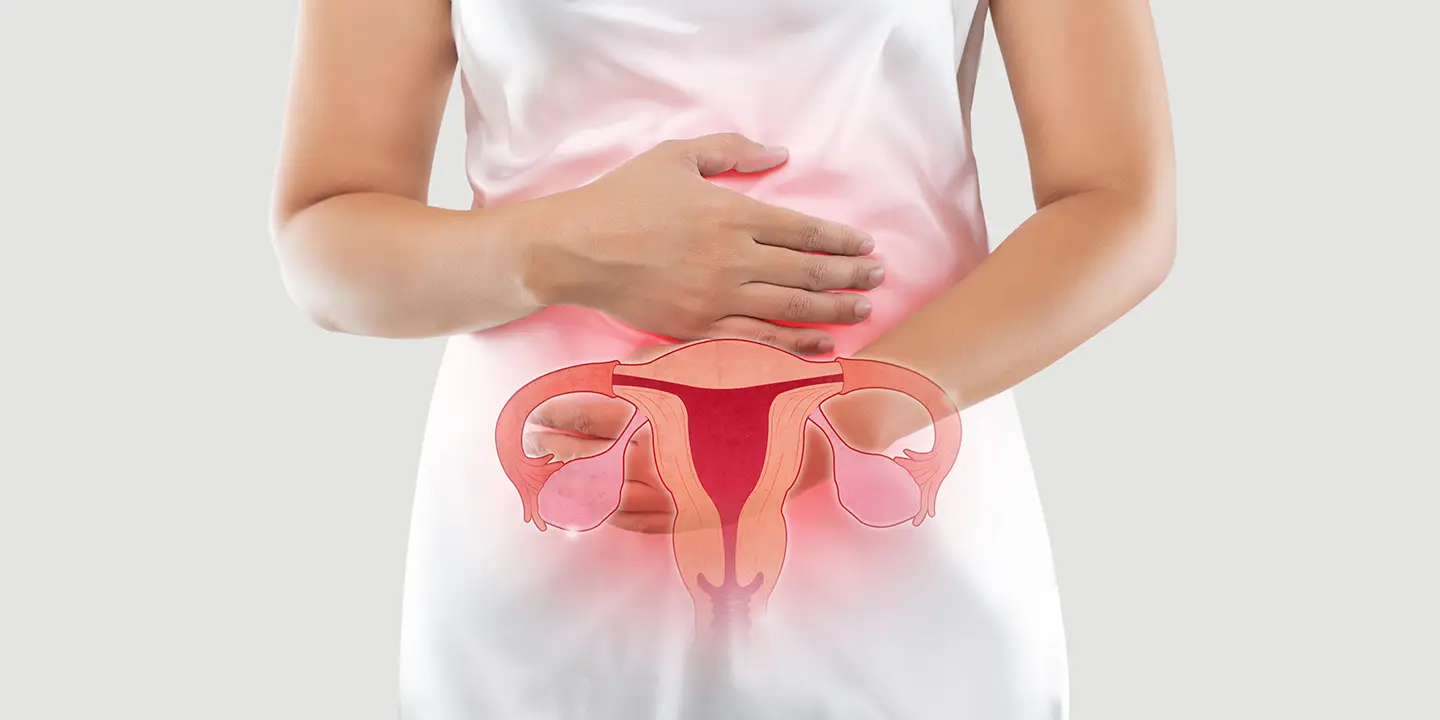
Ovarian cancer develops when cells in the woman’s ovaries start growing uncontrollably, and these cells have the power to invade surrounding tissues and can also spread throughout the body. Some tumours are not cancers because they cannot spread to other body parts and term benign or masses. The tumours are termed malignant tumours that can spread through the body or invade surrounding tissues. Many ovarian tumours are benign. Also, younger women get ovarian cysts, a fluid collection in ovaries that can cause pain. However, ovarian cysts are not cancerous. Your healthcare provider at QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY can suggest that you remove the cyst if it is painful and big. Ovarian cancer often causes no symptoms, and if you experience signs like bloating, feeling full, belly pain and needing to pee more often, then it is best to get yourself checked to start the treatment as early as possible. QUEEN’S GYNAECOLOGY can help you to determine the type of ovarian cancer and the right option for treatment.
In this Article
- 1 Ovarian cancer- early diagnosis is a must.
- 2 Causes of ovarian cancer
- 3 Ovarian cancer symptoms
- 4 Factors that decrease your risk of developing ovarian cancer
- 5 Ovarian cancer staging
- 6 Diagnosis of Ovarian cancer
- 7 Ovarian cancer treatment
- 8 How QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY can help you with ovarian cancer?
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 FAQ’s
Ovarian cancer- early diagnosis is a must.
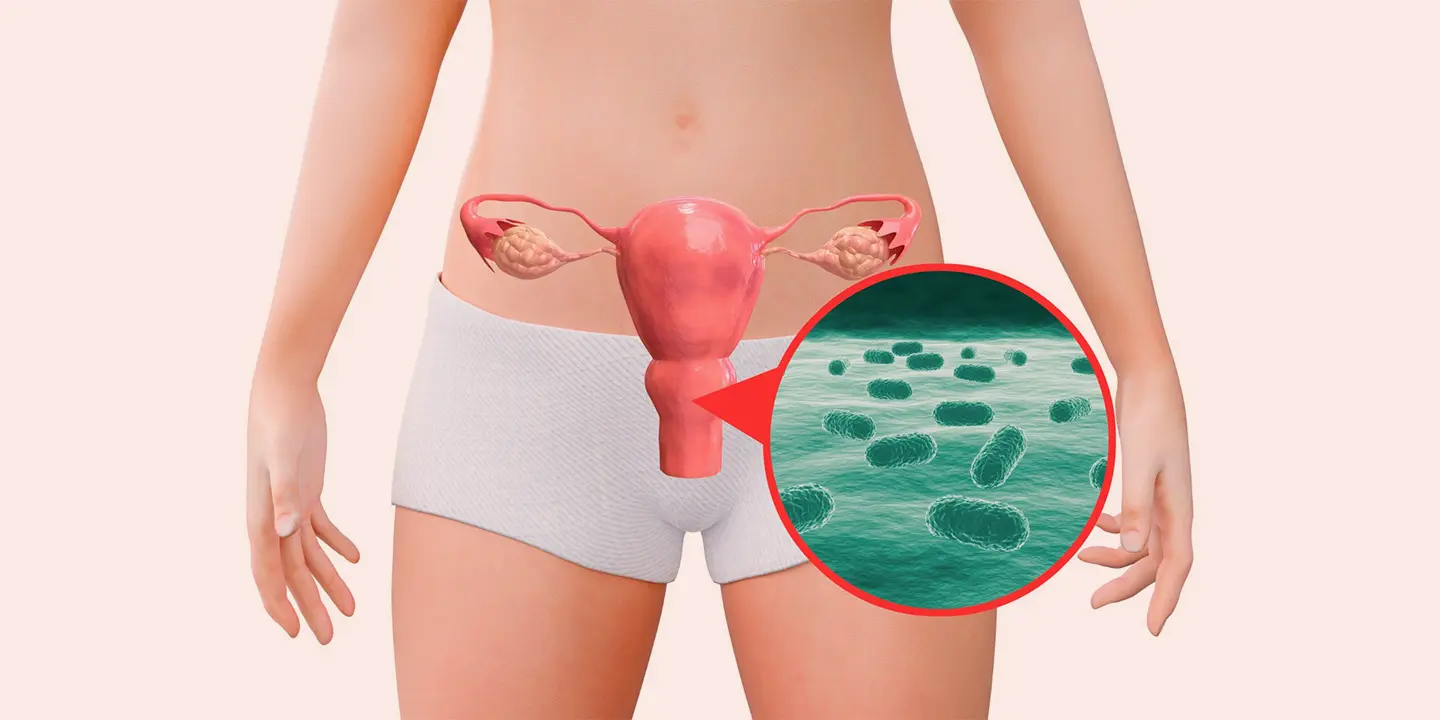
Ovarian cancer is one of the cancer types that begins in the ovary and develops when cells in the ovary grow uncontrollably. Some ovarian cancers also begin in the fallopian tubes that link the ovary to the uterus. In some cases, cancer cells in ovaries spread to the liver or elsewhere but are still called ovarian cancer. Three Ovarian tumour types are :
- The most common type is epithelial ovarian cancer, which comes from cells lying on the surface of the ovary. It generally makes up about 90 per cent of all ovarian cancers and develops in older women.
- The second ovarian type of ovarian cancer is germ cell ovarian cancer and strategies in ovarian cells that produce eggs and affect mainly younger women.
- The third type of ovarian cancer is stomach ovarian cancer in which the cancer develops from cells in the ovary that hold the ovary together and make hormones.
The above-listed ovarian cancer types are classified into more subtypes, and the classification is based on how wells look under a microscope. Ovarian cancer spreads from the pelvis to lymph nodes, stomach, liver, chest, abdomen and intestine.
Related Blog: 7 Signs Your Ovarian Cyst May Have Ruptured
Causes of ovarian cancer
The exact ovarian cancer causes are not known. However, some factors make a woman more prone to develop ovarian carcinoma. One of the causes of ovarian cancer is that it starts developing its cells at the tail of the fallopian tubes and not necessarily in the ovary itself. However, the most important risk factor is age, as older women are more prone to it, and the median age of diagnosis is 63. Also, women with genetic histories tend to be diagnosed with this type of cancer at a younger age. Some causes are :
- Getting older
- Inherited faulty genes or family history
- If you had breast cancer in the past, you are more likely to have ovarian cancer.
- Using hormone replacement therapy after menopause increases the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Smoking also makes you more prone to ovarian tumours.
- Medical conditions like diabetes or endometriosis make you more prone to ovarian cancer.
- Being obese
Ovarian cancer symptoms
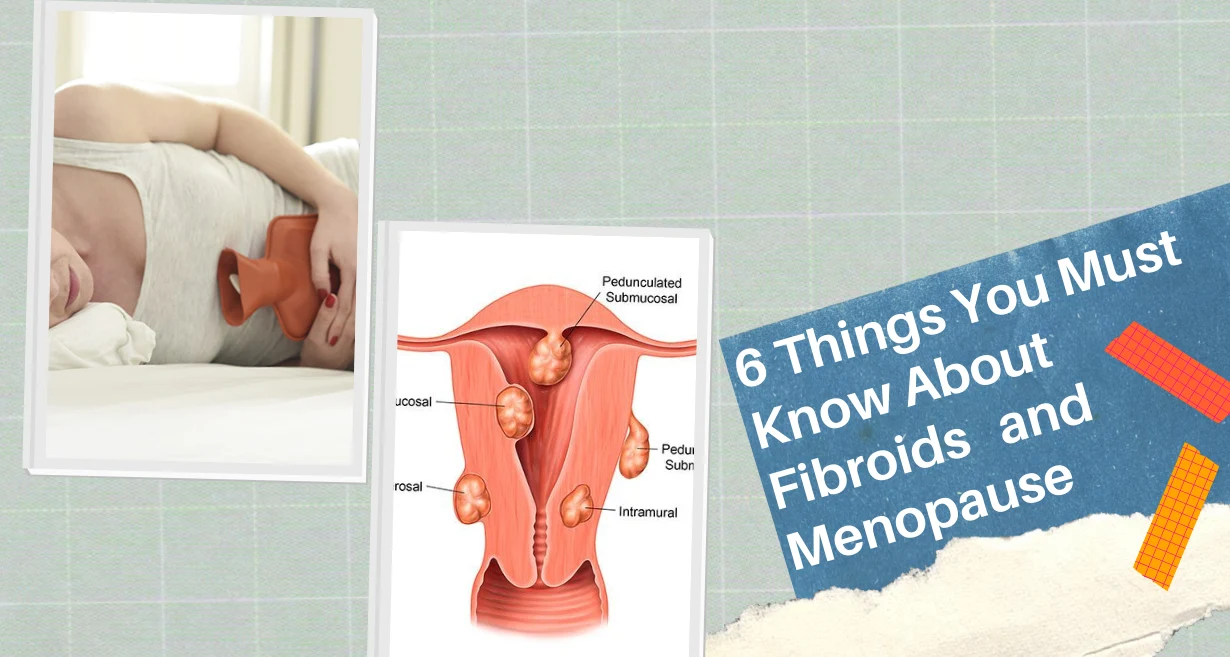
Early ovarian tumour symptoms like bloating, fullness, abdominal pain, and frequent urination can be ignored. Other symptoms of ovarian tumour comprise includes:
- Fatigue
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Sudden weight gain or weight loss
- Constipation
- Back pain
If you experience any of the above-listed symptoms for more than two weeks and are not typical, then it is best to consult a gynaecologist. They will help you to determine the exact cause and type of cancer. To diagnose, they recommend additional testing to see if your ovaries have abnormalities. The signs you experience may be non-cancer-related issues, but it’s good to have them checked and monitored by a doctor. Ovarian cancer can develop and spread throughout your abdomen before a person experiences any symptoms, which makes it difficult to detect early. Some more symptoms to check on :
- Abdominal pain
- Pelvic pain
- Changes in eating habits
- Vaginala discharge
- Bowel changes
Related Blog: What Size of Ovarian Cyst is Dangerous? Complete Guide
Factors that decrease your risk of developing ovarian cancer
According to experts, women who have used birth control for more than five years, who have given birth to a child, who have breastfed for more than a year or who have gone through a hysterectomy or else tubal ligation are less likely to develop ovarian cancer. The condition of ovarian tumour can be prevented by removing the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It is advised that women must consult an expert gynaecologist to discuss whether the surgery is appropriate for them or if there is any other treatment option for them. QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY helps you with all consultations and clarifies your doubts regarding ovarian tumours.
Ovarian cancer staging
Ovarian cancer staging clarifies how big the cancer is and whether it has spread or not. The tumour grade detects many things, like how abnormal the cells look under the microscope. Ovarian tumour classification is done in stages :
Stage 1 of ovarian cancer
The first stage of ovarian cancer is only in the ovaries, and surgery is the best option. Some women need chemotherapy at this stage. This stage is subdivided into three sub-stages: IA, IB and IC. The tumour is in a single ovary or fallopian tube in this substage2. In the second one, the tumour is in both ovaries or fallopian tubes and in this sub-stage, cancer is in both ovaries and is also found outside the ovary.
Stage 2 of ovarian cancer
In the second stage, the cancer has grown outside the ovaries and within the pelvis. For this, also best treatment option is surgery as well as chemotherapy. The stage is subdivided into stage IIA, in which cancer is no longer only in the ovary but also spreads to the uterus. In the next step, IIB, the cancer has spread to other nearby structures in the pelvis.
Stage 3 of ovarian cancer
The third stage of ovarian cancer tests that it has spread outside the pelvis into the abdominal cavity or lymph nodes, and it can be treated by surgery as well as chemotherapy. The stage is again subdivided into three substages. In the first sub-stage IIIA, cancer has spread beyond the pelvis to the abdomen or within lymph nodes. In the second sub-stage IB, the tumour is up to 2 cm in size and spreads beyond the pelvis. At this sub-stage, IC cancer has moved outside the pelvis area and is larger in size, and it can also impact other organs at this point.
Stage 4 of ovarian cancer
The fourth stage of ovarian cancer is when cancer has spread to other body parts as well as some distance away from the real ovary, like the liver or lungs, and the primary treatment for this stage of ovarian tumour is chemotherapy and surgery. The stage is categorized into two substages IVA, in which cancer is near the lungs, and in stage IVB, the cancer spreads to lymph nodes of your groin or into the chest.
Diagnosis of Ovarian cancer
CA 125 is a biomarker for ovarian cancer; it stands for Cancer Antigen 125, a protein that may be present in high amounts in the blood of people with ovarian cancer. It is among the blood tests doctors recommend if ovarian cancer is suspected and a person experiences ovarian cancer symptoms. The test is also used to monitor how well the treatment s working because CA 125 level fluctuates in response to treatment. Your gynaecologist will ask about your medical history to learn about possible risk factors and likely do a pelvic exam to check for enlarged ovaries or signs. However, transvaginal ultrasound is the foremost test used if a person is detected with issues in the ovaries. A gynaecologist will help you to detect ovarian cancer and also help you to get the best kind of surgery. To diagnose the tumour doctor recommends many tests, including.
- Imaging tests like ultrasound CT scans, barium enema X-ray
- MRI scan
- Chest X-ray
- PET Scan
- Laparoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy
A doctor will also recommend many other blood tests, including CA 125, and an expert gynaecologist will monitor women with high levels.
Related Blog: Ovarian Cyst and its Impact on Pregnancy and Fertility
Ovarian cancer treatment
Ovarian cancer treatment aims to remove as much, if not all, cancer in a person’s body. Common treatment options are:
- Surgery
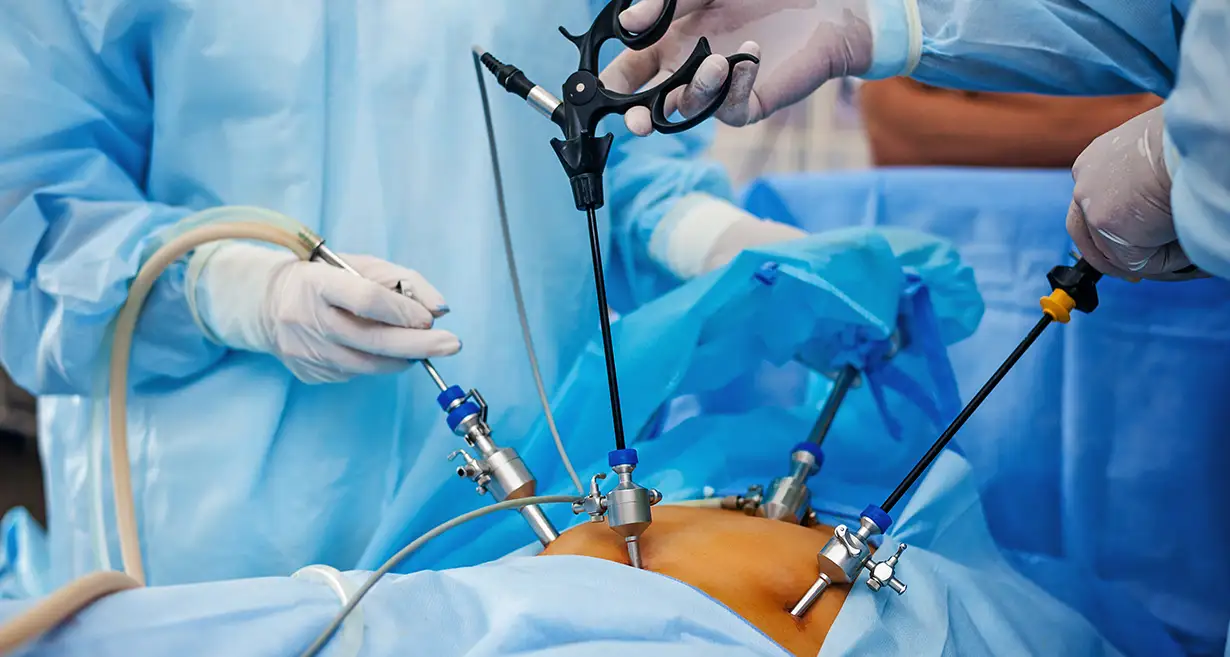
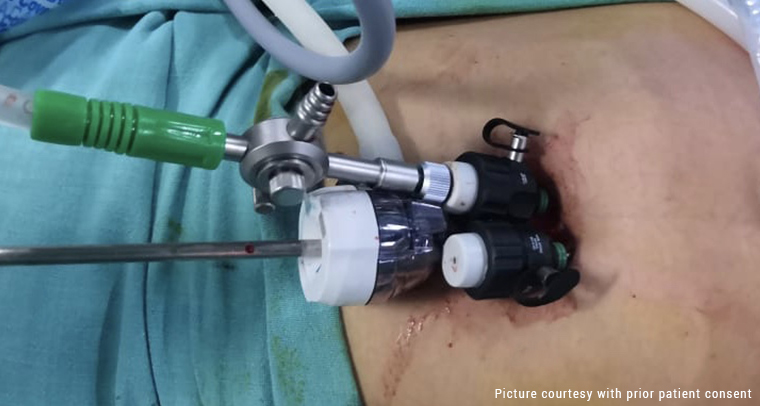
It is one of the treatments for ovarian cancer that involves the removal of reproductive organs and any organ with cancer on it. The expert surgeon will use laparoscopy for minimally invasive surgery and laparotomy for open surgery requiring an abdominal incision.
- Chemotherapy
It is recommended either before or after the surgery and are drugs designed to target and kill cancer cells. A patient will be provided chemo through a vein or orally through a pill.
- Targeted therapy
This is a cancer treatment done by using drugs to identify and attack cancer cells. It helps to alter the way cells grow and divide.
- Radiation therapy
It is used rarely by the doctor but is used in a few cases.
After completing the ovarian cancer treatment, the expert doctor will want you to see them for regular follow-ups for observation. You have to visit the specialist to ensure the cancer has not returned. The doctor may also go through any possible symptoms and recommend any test like an imaging test, generally a CT Scan.
How QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY can help you with ovarian cancer?
We at QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY believe in the timely diagnosis of anomalies. In most cases, women need to be made aware of the findings as many conditions are determined to be incidental during other investigations and treatments. The main aim of our expert doctors is to identify anomalies using the latest modalities, such as 3d/4d ultrasound, laparoscopy and hysteroscopy and start early treatment simultaneously. Laparoscopic surgery is a commonly performed as well as safe procedure when performed by an experienced surgeon. However, like any other procedure, the risk of any is determined by the nature of the surgery; a person’s health and various medical conditions also affect the risk of surgery. It is better to discuss all your concerns with your gynaecologist beforehand. Our experts at QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY are always there to help you and clarify all your queries.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is one of the common causes of death in women, and it should be diagnosed early for better chances of curing and to avoid high mortality rates. If ovarian cancer is detected early and confined to stage 1, patients have about 92 per cent survival rates depending on the type of cancer. It is best to consult with a gynaecologist at the first sign of ovarian tumour symptoms. QUEEN’S GYNECOLOGY is here for you to offer comprehensive, high quality and innovative care for patients whose family history or personal health increases their risk of cancer. The clinic works with cutting-edge technology, board-certified gynecologic oncologists that team up and create a personalised prevention and care plan for every patient.
FAQ’s
Ovarian cancer is mainly asymptomatic, and because there is no detection at the early stage, it makes it more difficult to treat successfully.
Yes, it is because if any family member has breast cancer, you may be at a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer. The reason behind it is that both cancers share the same risk factors.
Some ovarian tumours cause abnormal vaginal bleeding and even missed periods. Most ovarian tumours are non-cancerous, and missed periods do not always indicate ovarian cancer. Irregular periods rarely show serious issues but may increase ovarian cancer risk.
Many people believe that if they clear the Pap test, they have bo ovarian cancer, but this is not the case. Pap tests diagnose cervical disease and are not a tool to detect ovarian cancer. You have to go for CA 125 test, which is used to detect ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer treatment can cause physical changes that affect how you feel, as you may experience hair loss, Hormonal changes and tiredness.
The worst part about ovarian cancer is that it is asymptomatic and often diagnosed late. Symptom awareness can help a person for quicker diagnosis as diagnosing it before it spreads makes it more treatable.
There is no way of preventing ovarian cancer, but certain things are associated with lower chances of developing it. Breastfeeding is one of them as it reduces the risk.