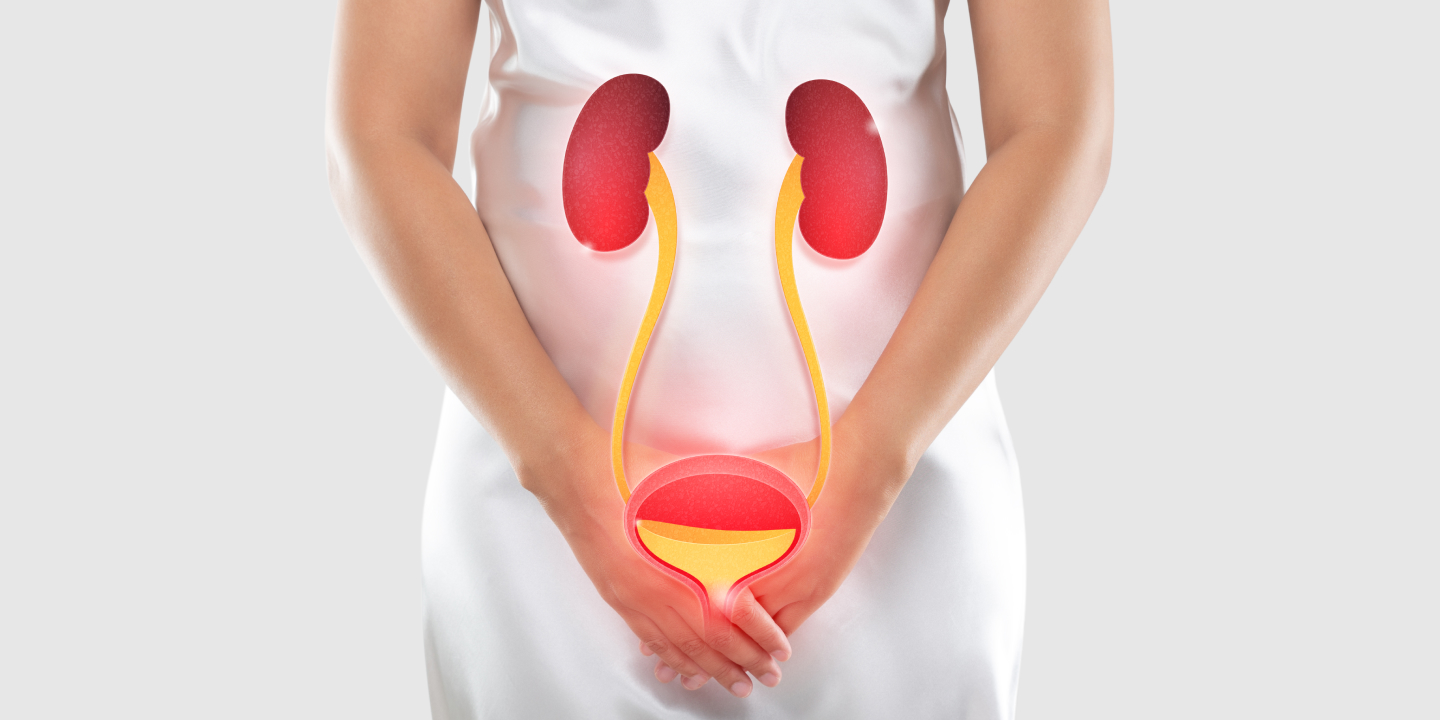
UTIs, or Urinary Tract Infections, are among women’s most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Recurrent UTIs indicate the repeated occurrence of the infection within a specific timeframe, typically defined as two or more infections in six months or three or more infections in one year.
The onset of recurrent UTIs is not only a complication for one’s health but also leads to long-term and chronic complications related to one’s renal or reproductive health. Understanding the underlying causes, risk factors, and effective management strategies for recurrent UTIs is essential to alleviating the suffering of affected individuals.
This article will explore everything there is to know about frequent UTIs in females, their potential causes, and the treatments available.
Related Blog: What Is UTI Infection? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment infection of Urinary Tract Infection in Female
In this Article
Understanding The Basics of Recurrent UTI
Before we delve into the concept of Recurrent UTI, let us explain what a UTI is and the kind of risks it imposes on the body.
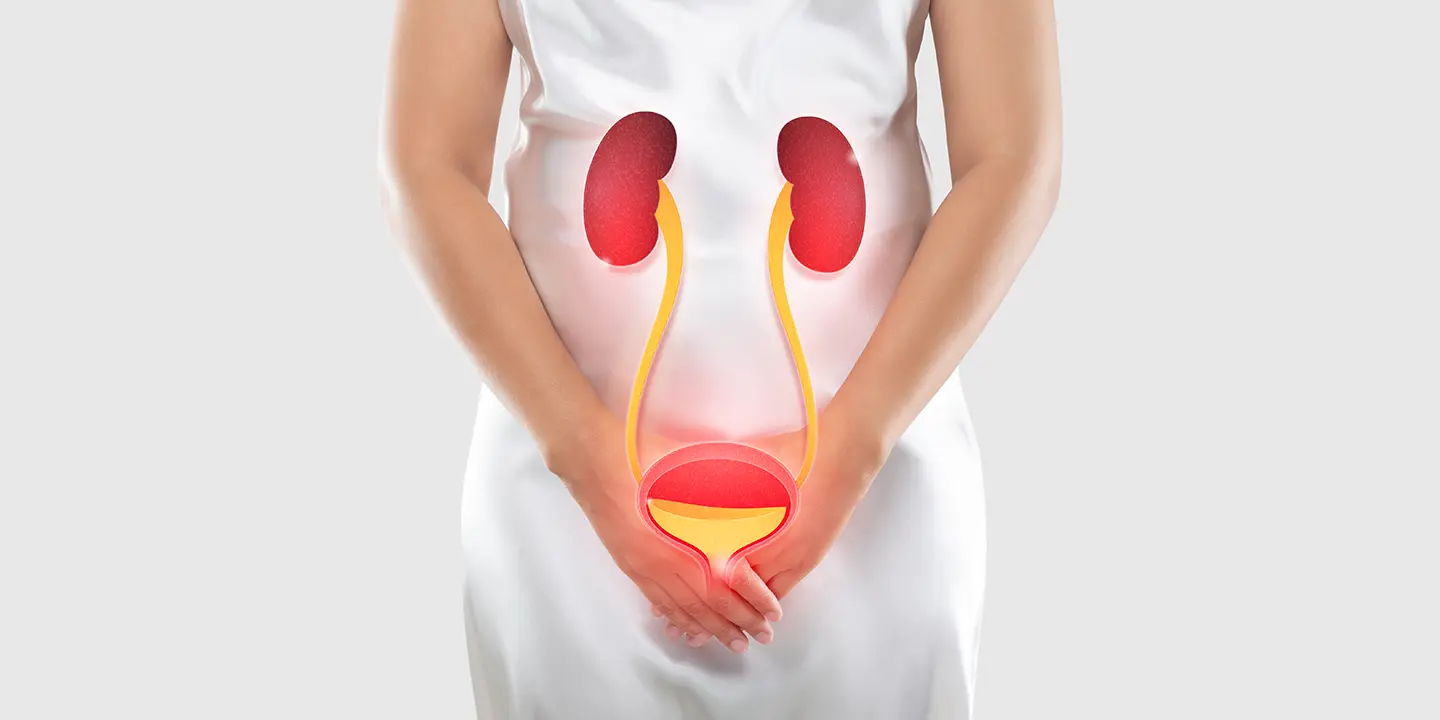
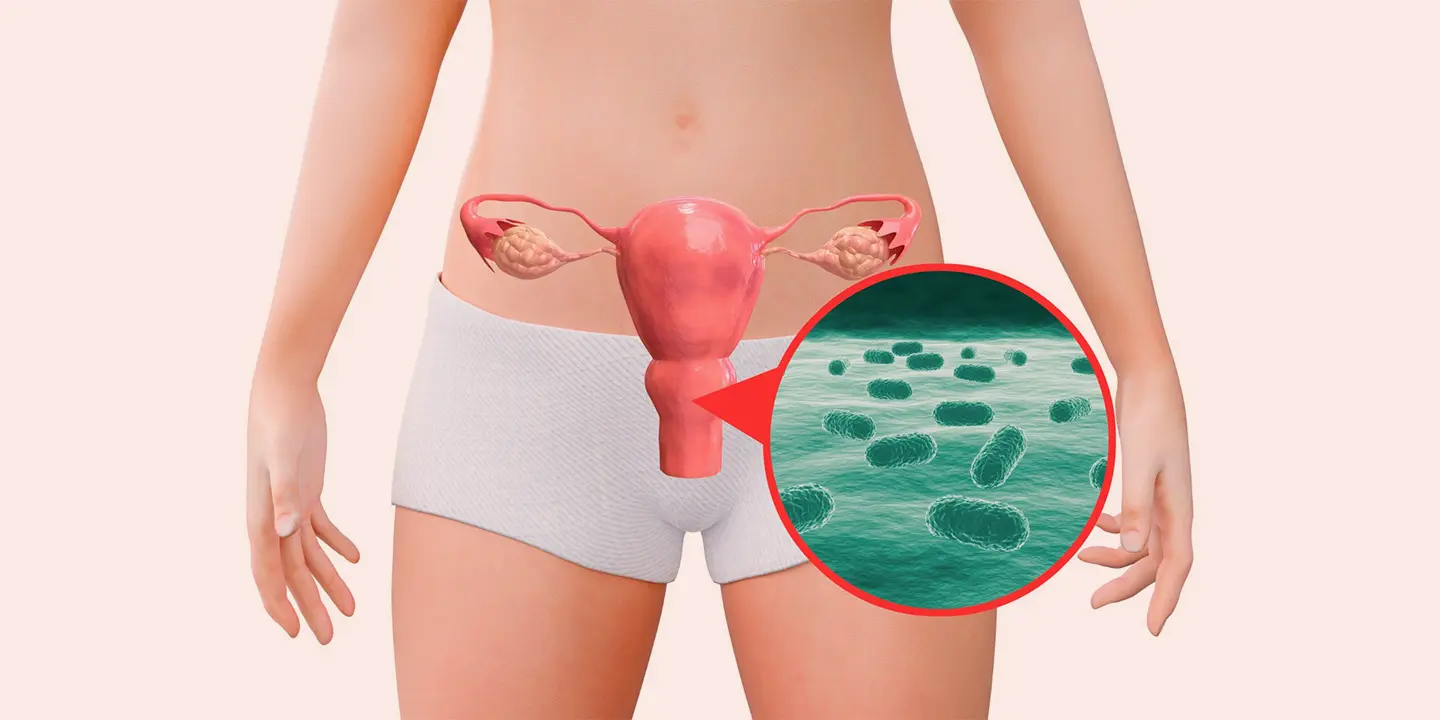
UTIs are bacterial infections that can affect or occur in any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, ureter, or urethra. The majority of UTIs that are diagnosed occur in the lower urinary tract, especially around the urinary bladder and the urethra.
Recurrent UTIs, as we previously explained, are a persistent onset of infection wherein the infection occurs two or more times in six months or three or more times in a single year.
Recurrent UTIs can manifest as recurrent episodes of cystitis, urethritis, or pyelonephritis, which indicate that they can happen both in the upper and lower parts of the urinary tract.
What are the Potential Causes of Recurrent UTIs?
Chronic urinary tract infections are bacterial infections that are recurrent in nature or fail to respond to ongoing treatment due to multiple reasons.
Following are a few potential triggers behind the onset of recurrent UTIs in females:
- Female anatomy and physiology Compared to men, women have a shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder, increasing the risk of UTI. Furthermore, certain hormonal fluctuations and indulging in unprotected sexual intercourse can also lead to the onset of UTIs and their recurrence in the future.
- Catheter use: Indwelling urinary catheters are another potential cause that leads to the onset of UTIs and even imposes the risk of recurrent UTIs in women. This is a common risk in healthcare settings like hospitals and nursing homes.
- Sexual activity: One of the most common recurrent UTI causes is sexual activity. Unprotected sexual activity can facilitate the entry of bacteria into the urinary tract, especially the urinary bladder and urethra, further increasing the risk of UTI in the individual.
- Impaired immune function: Patients with a weakened immune system are also at risk of developing recurrent UTIs. This can be a consequence of taking certain medications or due to an autoimmune disorder as well.
- Urinary tract anomalies: Potential structural abnormalities in the urinary tract can also contribute to the onset of recurrent UTIs in women and children.
- Antibiotic resistance: The indiscriminate use of antibiotics has contributed to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, complicating the treatment of recurrent UTIs. Resistant strains can persist in the urinary tract, leading to recurrent infections that are challenging to eradicate.
- Persistent bacterial infections: In some cases, conditions like bacterial reservoirs known as biofilms occur in the urinary tract. These protect the bacteria in the urinary tract from the prescribed and administered antibiotics, further contributing to their recurrence.
- Hormonal imbalance: As weird as it sounds, recurrent UTIs in females can occur due to hormonal changes during menstruation or menopause. Since it directly alters the vaginal environment, it triggers the risk of recurrent UTIs.
Understanding the individual causes of recurrent UTIs in women is crucial for a comprehensive and holistic diagnosis and treatment.
What are the Symptoms of a recurrent UTI?
Now that you clearly understand the potential list of causes, let us walk you through the symptoms that are quite common in patients experiencing recurrent UTIs.
Some of the common symptoms include:
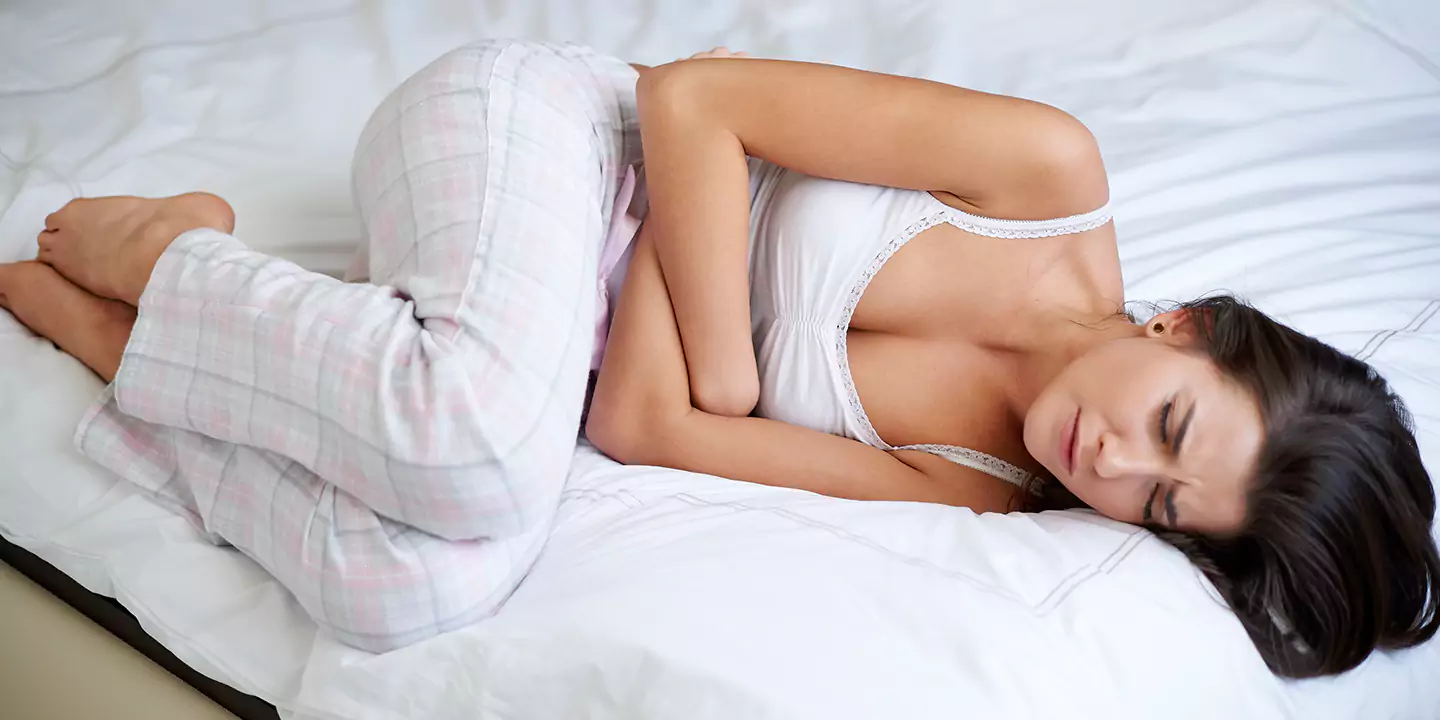
- Frequent urination
- Dark-colored or bloody urine
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Pain and discomfort around the kidneys
- Pain in the bladder region
These are some of the most telltale signs of a recurrent UTI. However, you need to understand that the above symptoms occur if the infection is contained within the urinary tract and hasn’t affected or reached the kidneys. If the infection reaches the kidneys, it can lead to a list of severe symptoms, including:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Chills
- High-grade fever
- Fatigue
- Mental disorientation, etc.
Irrespective of the severity of the symptoms, UTIs, especially recurrent UTIs, require medical intervention for quicker treatment and recovery. If you are “letting it be,” that’s another common risk contributing to the recurrence of the UTI in the patient.
Who is Primarily at Risk of Developing Recurrent or Chronic UTIs?
Recurrent UTIs are mostly common in women. However, it can present and manifest in different ways, which we will discuss at length.
In women
Women are generally at heightened risk of developing chronic UTIs for two primary reasons:
The anatomical disparity suggests that the urethra is placed closer to the rectum in females, facilitating easy movement of the bacteria and increasing the risk of infection.
Also, as we mentioned before, women have a shorter urethra, making it more accessible for bacteria to travel through it and leading to the development of bacterial infections.
In men
Although it is true that women are more predisposed to the development of recurrent UTIs, recurrent UTIs in men are also a possibility. In men, the most common reason is an enlarged prostate.
But the question is, “How?”
When the prostate gland is enlarged, it obstructs the bladder, making it difficult to empty it entirely. The residual urine in the bladder often leads to the risk of recurrent UTIs.
In menopause
Menopause in women introduces a plethora of hormonal imbalances in the body, which, in turn, contribute to changes in the vaginal environment. This further escalates the risk of recurrent UTIs as well.
Understanding the risk factors is a great way to prevent the onset of recurrent UTIs in individuals in the long run.
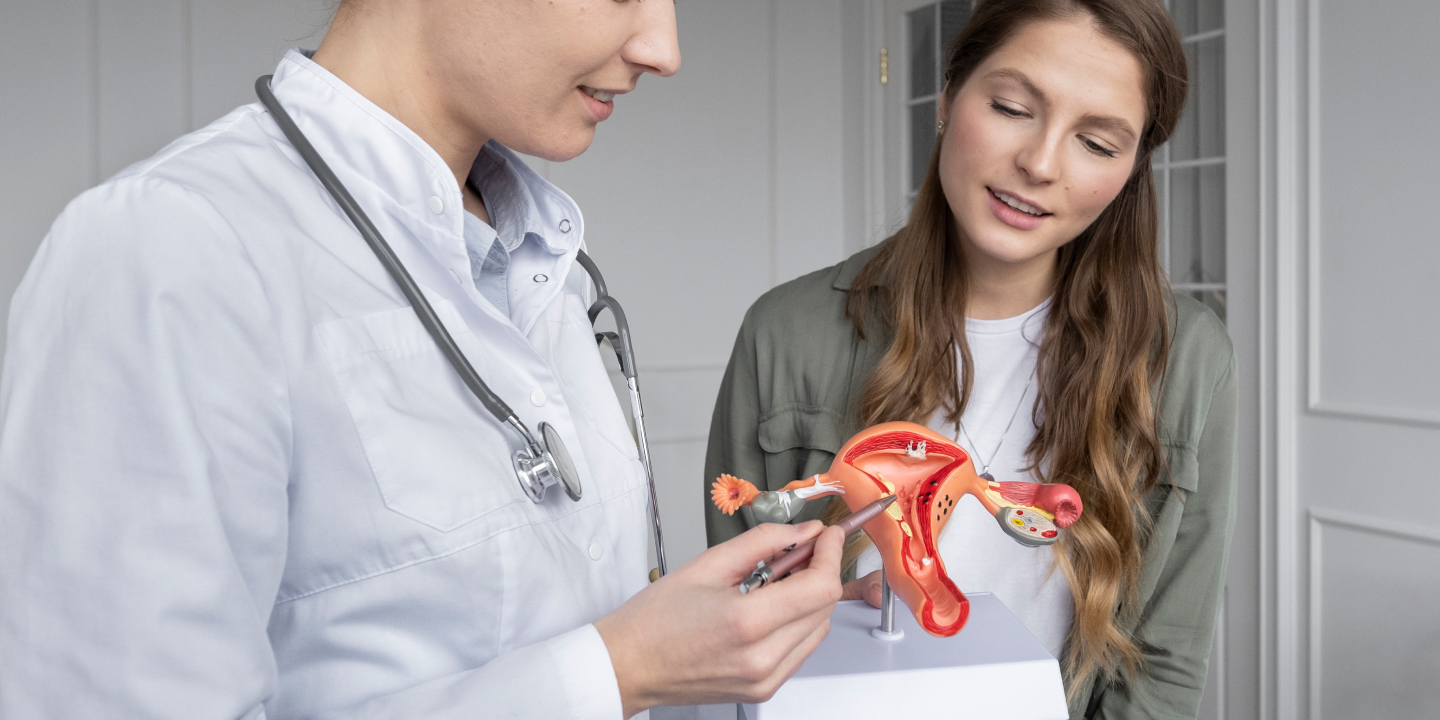
Diagnosis of Recurrent UTI
Recurrent UTI or chronic UTI means that you have a history of urinary tract infections. Given the severity of the condition and discomfort, one must get a timely diagnosis for a quicker recovery.
- The most common route for UTI diagnosis is via a urine culture test. In this test, a urine sample is collected from the patient and sent to the laboratory to check for bacterial growth. The culture takes 1–3 days to assess the treatment better.
- In cases where the doctor suspects potential risks of kidney damage, further testing and imaging are prescribed. X-rays and kidney scans are common in those cases.
- The last form of diagnosis for recurrent UTIs is cystoscopy. This involves using a cystoscope, which helps look inside the bladder and urethra to detect abnormalities or other complications in the urinary tract.
Following a comprehensive diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan is crafted for the patient to help them overcome the symptoms and improve their quality of life.
How are Recurrent UTIs Treated?
Chronic UTI treatment involves two primary routes: medications and natural remedies. Let us explore those in detail:
1. Antibiotic therapy
The most common treatment route for recurrent UTIs is antibiotic therapy, typically prescribed for around one week.
However, patients suffering from recurrent or chronic UTIs might benefit from long-term and low-dose antibiotics since the symptoms often recur, leading to further complications. Ongoing medication therapy effectively prevents the symptoms from recurring in the future.
Besides ongoing antibiotics and allied medications, the urologist or gynecologist you consult will further monitor the urinary tract system.
At Queen’s Gynecology, we prioritize effective and sustained treatment that will prevent the onset of urinary tract infections in patients in the future.
2. Natural remedies
There are a plethora of natural remedies that are found to be quite beneficial in treating cases of recurrent UTIs. Among them, drinking cranberry juice is an effective measure that reduces the risk of chronic UTIs.
Studies indicate that cranberry destroys the natural biofilms of bacteria in the urinary tract, making it difficult and almost impossible for the bacteria to colonize the urinary tract. Multiple cranberry products include cranberry juice, supplements, and even extracts.
Besides this, probiotics are also an effective way to manage cases of recurrent UTIs. They balance the beneficial bacteria in the urogenital tract, preventing the risk of pathogenic growth.
Another natural remedy that’s important to pay attention to is D-Mannose. It has been studied to reduce the recurrence of UTIs and promote effective recovery. A doctor’s proper prescription and advice are mandatory, irrespective of the kind of natural remedy you opt for.
Recurrent UTIs impose significant physical, emotional, and financial burdens on individuals and healthcare systems, necessitating effective preventive and treatment approaches.
Conclusion
Recurrent UTIs shouldn’t be “left to recover” by themselves. Not opting for the required treatment can lead to kidney infections and sepsis, which can be life-threatening. Given how badly recurrent UTIs affect one’s quality of life, it isn’t surprising that there is an increased need for timely diagnosis and treatment.
At Queen’s Gynecology, our team of experienced gynecologists is here to offer a comprehensive diagnosis and holistic treatment that stops the cycle of recurrent UTIs and ensures a quicker recovery. For more details regarding appointments, contact us directly at +91 9654999888.
FAQ’s
Recurring UTIs impose many complications if left untreated. Some of the most notable ones include kidney infections, sepsis, septicemia, and even increased risks of preterm delivery in pregnant women.
Some of the important lifestyle modifications that can effectively reduce the risks of UTI include ensuring proper hydration, maintaining optimal personal hygiene, ensuring protected sexual intercourse, etc.
The list of male urinary tract infection symptoms is the same as the ones noted in females. They include frequent urination, a burning sensation while urinating, dark-colored urine, abdominal pain, etc.